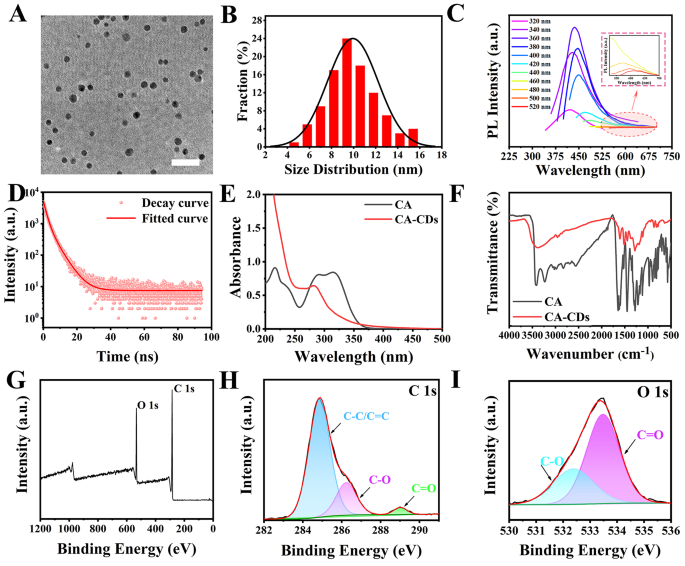
Characterization of the CA-CDs
The CA answer was clear and confirmed little fluorescence below 365 nm UV lamp, whereas the ready CA-CDs answer was pale yellow below mild and confirmed yellow-green fluorescence below 365 nm UV irradiation (Fig. S1). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) picture confirmed that the CA-CDs had relative uniform measurement and good dispersion, with a mean measurement of 9.70 ± 0.10 nm (Fig. 1A and B). The CA-CDs exhibited excitation-dependent traits (Fig. 1C). On the optimum excitation wavelength of ~ 360 nm, the emission wavelength of the CA-CDs was ~ 420 nm. The fluorescence decay curve of the CA-CDs was fitted in accordance with the second-order decay index operate (Fig. 1D). Two fluorescence lifetimes (τ) had been obtained, indicating that the CA-CDs had two fluorescence facilities (Desk S1). The common lifetime of the CA-CDs was ~ 3.24 nm and the quantum yield was ~ 0.8%.
The CA answer had three absorption peaks at ~ 216 nm, ~ 291 nm, and ~ 314 nm, respectively (Fig. 1E), indicating the presence of benzene ring and conjugated carbonyl group within the compound. The extensive absorption at ~ 258 nm and the absorption peak at ~ 280 nm of the CA-CDs answer revealed the presence of π–π*, n–π* digital transitions, indicating the presence of C = C, C = O, and C-O on the CA-CDs floor [35]. Fourier rework infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) confirmed that CA had absorption peaks at 3417, 3228, 1639, 1524, 1293, 1210 and 1117 cm− 1, which had been associated to the growth and contraction vibrations of the practical teams O-H, C-H, C = O, C = C and C-O (Fig. 1F). Whereas for the CA-CDs, the absorption peak at ~ 3380 cm− 1 belonged to the growth vibration of O-H bond, the absorption peak at ~ 2920 cm− 1 belonged to the presence of C-H bond, the absorption at ~ 1600 cm− 1 belonged to the growth vibration of C = O, the absorption at ~ 1500 cm− 1 was the growth vibration of benzene ring skeleton, and the absorption at ~ 1196 cm− 1 was the growth vibration of C-O. XPS full-spectra scan confirmed that each CA and the CA-CDs had been composed of C and O parts (Fig. S2 and Fig. 1G). The high-resolution C1s spectra of the CA-CDs had distinct peaks at 284.8 eV, 286.3 eV, and 288.5 eV, which associated to the presence of C = C/C-C, C-O, and C = O, respectively (Fig. 1H) [36]. The attribute peaks at ~ 531.9 eV and ~ 533.5 eV within the high-resolution O1s spectra correspond to the C-O and C = O teams, respectively (Fig. 1I). The atomic ratios of C and O in CA had been ~ 71.65% and ~ 28.35%. The corresponding atomic ratios of the CA-CDs had been ~ 78.14% and ~ 21.86%. It instructed that hydrothermal synthesis triggered the partial chemical bonds of CA to interrupt and reassemble throughout the fabrication of the CA-CDs. The change within the atomic ratio was the results of the formation of CDs by means of carbonization [37]. The above outcomes indicated that the CA-CDs retained a part of the construction of CA, and the floor was wealthy in -OH and -COOH teams.
Structural characterization of the CA-CDs. (A) (B) TEM picture and measurement distribution of the CA-CDs, the size bar was 50 nm. (C) Fluorescence spectra of the CA-CDs at completely different excitation wavelengths of 320 ~ 520 nm. (D) Fluorescence attenuation curve of the CA-CDs. (E) UV-Vis absorption spectra of CA and the CA-CDs (0.2 mg/mL) in aqueous answer. (F) FT-IR spectra of CA and the CA-CDs. (G) Excessive-resolution XPS spectra of the CA-CDs: C1s spectra (H) and O1s spectra (I)
The soundness of nanomedicine is a vital indicator to measure whether or not it may be utilized. First, the steadiness of the CA-CDs in a large focus vary of NaCl (0–1.0 mol/L) and KCl (0–1.0 mol/L) was examined. It may be seen that the rise in NaCl and KCl concentrations hardly affected the fluorescence depth of the CA-CDs (Fig. S3A and S3B). The outcomes confirmed that the CA-CDs had good salt resistance, and their construction and properties could be much less affected in organisms (the focus of regular salts in regular physique fluids is ~ 0.15 mol/L). The CA-CDs had been irradiated at 365 nm ultraviolet for 180 min. The fluorescence depth of the CA-CDs additionally modified little, implying that the CA-CDs had good photobleaching resistance (Fig. S3C). As well as, contemplating using the CA-CDs is as a drug, the steadiness had been additionally examined within the phosphate-buffered saline, RPMI 1640 media, fetal bovine serum and penictomycin combination (Fig. S4). There have been some little adjustments of the fluorescence properties of the CA-CDs. It instructed that the CA-CDs had been secure in difficult bioenvironments.
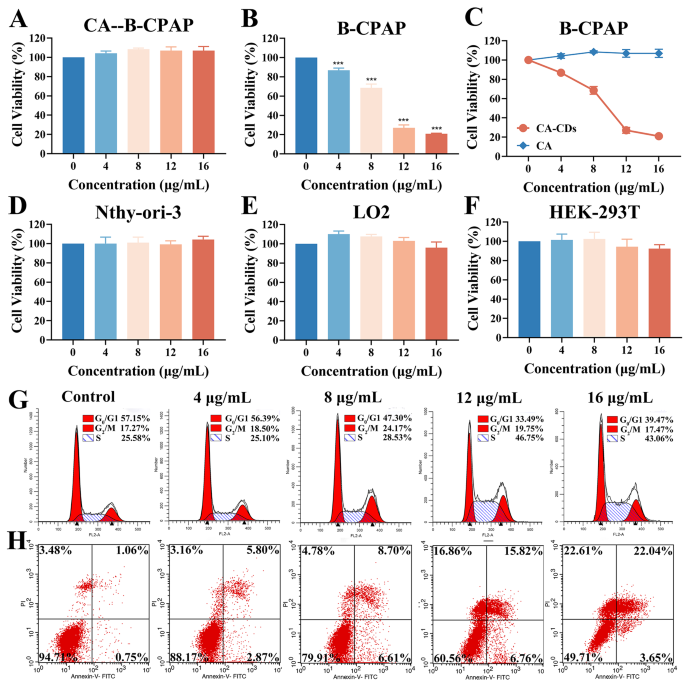
In vitro inhibition impact of the CA-CDs on BCPAP cells
Primarily based on the above good bodily and chemical properties of the CA-CDs, the organic exercise of the CA-CDs in vitro was studied by Cell-Counting-Package-8 technique (CCK-8). After 48 h of co-incubation, low-dose CA-CDs confirmed a big inhibitory impact on the proliferation of the papillary thyroid most cancers cells BCPAP (Fig. 2A). Because the dosing focus elevated, the cell viability decreased clearly. At concentrations of 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL of the CA-CDs, inhibition charge of the BCPAP cells reached ~ 73% and ~ 79%, respectively. In distinction, CA confirmed little impact on the cell viability of the BCPAP cells (Fig. 2B). As a pure natural drugs, CA ought to have many organic actions. Nonetheless, as a result of poor water solubility and low cell membrane permeability of CA molecules, the bioavailability and medicinal worth of CA molecules have been severely hindered. The above experiments have demonstrated that the CA-CDs had sure hydrophilic teams on the floor, might be uniformly dispersed in water, and retained a part of the structural of CA. Thus, the CA-CDs could possess sure organic exercise. When the CA-CDs had been co-incubated with the BCPAP cells, they are often engulfed by means of the cells in giant portions owing to their nanometer measurement and floor practical teams, and thereby exerted environment friendly drug results (Fig. 2C) [7, 8]. As well as, CCK-8 evaluation demonstrated low biotoxicity of the CA-CDs on regular thyroid cells Nthy-ori-3, hepatic regular cells LO2, and renal regular cells HEK-293T below the identical circumstances (Fig. 2D, E and F). These outcomes instructed that the CA-CDs might be thought of as a possible nanodrug in opposition to papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Results of the CA-CDs on viability, cycle, and apoptosis of the BCPAP cells. (A) Impact of the CA-CDs on the viability of the BCPAP cells. (B) Impact of CA on the BCPAP cell viability. (C) Statistic diagram evaluating the consequences of CA and the CA-CDs on the BCPAP cell exercise. Impact of the CA-CDs on the cell exercise of Nthy-ori-3 (D), LO2 (E) and HEK-293T (F). (G) .Stream cytometry cycle diagram of the BCPAP cells after 48 h remedy with the CA-CDs (0 µg/mL, 4 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL). (H) Apoptosis of the BCPAP cells after 48 h remedy with the CA-CDs (0 µg/mL, 4 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 in comparison with Management
The cell cycle is carefully associated to cell proliferation. Stream cytometry confirmed that a lot of the BCPAP cells of Contral group (CA-CDs 0 µg/mL) had been within the G0/G1 part, with fewer cells within the S part and the smallest proportion of cells within the G2/M part. The proportion of S part of the BCPAP cells elevated after 48 h handled with completely different concentrations of the CA-CDs (4 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL) (Desk S2). Particularly, after remedy with the CA-CDs at concentrations of 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL, the proportion of the BCPAP cells in S part was as excessive as ~ 46% and ~ 43% (p < 0.001, p < 0.01), indicating that the CA-CDs might arrest the BCPAP cells in S part (Fig. 2G). After 48 h of incubation with the CA-CDs (4 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL), the apoptosis of the BCPAP cells was detected by a move cytometry. The proportion of early apoptosis and late apoptosis of the BCPAP cells within the Contral group (CA-CDs 0 µg/mL) was ~ 1.07% and ~ 1.58%, respectively. The proportion of early apoptosis and late apoptosis of the BCPAP cells within the most administration remedy group (CA-CDs 16 µg/mL) was ~ 5.31% and ~ 30.16%, respectively (Desk S3), indicating the considerably enhance of apoptosis charge (p < 0.05, p < 0.001). The outcomes confirmed that the low-dose CA-CDs might considerably induce the BCPAP apoptosis, and the apoptosis charge was positively correlated with the dose of the CA-CDs (Fig. 2H).
With a purpose to additional discover the inhibitory impact of the CA-CDs on the BCPAP cells, the entry of the CA-CDs into the BCPAP cells at completely different incubation occasions was monitored by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 3). In brightfield, it might be seen that with the extension of incubation time, the BCPAP cells progressively shrank and have become rounded, and the cell morphology was disrupted. It may be seen that the CA-CDs can successfully enter the cells and emitted inexperienced and pink fluorescence below completely different mild irradiation. After co-incubation for 0 ~ 24 h, the fluorescence depth of the system progressively elevated, indicating that the variety of intracellular CA-CDs elevated with time. The fluorescence depth of the system was the very best at 24 h, indicating that the BCPAP cells had the very best uptake of the CA-CDs. From 24 to 48 h, the fluorescence depth of the system decreased, and the fluorescence was nearly undetectable at 48 h. This can be as a result of structural destruction of the intracellular CA-CDs by reacting with the cell matrix, accompanied with the gradual shrinkage and dying of the BCPAP cells. The change of fluorescence depth within the incubation system instructed that the inhibitory impact of the CA-CDs on the BCPAP cells was time-dependent. As well as, the uptake of the CA-CDs by the LO2 cells and the Nthy-ori-3 cells at completely different occasions was additionally noticed (Fig. S5 and S6). The LO2 cells and the Nthy-ori-3 cells exhibited related uptake properties of the CA-CDs, in contrast with the BCPAP cells. It implies that the CA-CDs will also be taken up by the conventional cells, however carried out little inhibition on these cells.
Distribution of the CA-CDs in BCPAP cells with time. Fluorescence microscopy photographs of the CA-CDs (30 µg/mL) and the BCPCP cells below brightfield and fluorescence fields (fluorescence excitation wavelengths 488 nm, 405 nm and 516 nm) after co-incubation for various occasions (0 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h). The dimensions bars had been 100 μm
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are additionally an essential think about most cancers remedy analysis. Elevated ROS ranges can induce apoptosis by means of each endogenous and exogenous pathways. Right here, the adjustments in ROS fluorescence depth within the BCPAP cells after handled with completely different concentrations of the CA-CDs (4, 8, 12, and 16 µg/mL) had been noticed by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 4A). In contrast with the management group (0 µg/mL CA-CDs), the common intracellular ROS pink fluorescence depth was a lot stronger when the focus of the CA-CDs reached 12 µg/mL (p < 0.01). When the focus of the CA-CDs reached 16 µg/mL, the intracellular ROS pink fluorescence was additional considerably enhanced. The pictures in brightfield additionally confirmed that with the rise of the CA-CDs administered focus, the morphology of the BCPAP cells shrunk and rounded, and the variety of the cells decreased clearly (Fig. S7). These outcomes confirmed that the CA-CDs might inhibit the BCPAP cells by triggering a considerable amount of ROS manufacturing in cells. After 48 h of remedy with the CA-CDs (0, 4, 8, 12, and 16 µg/mL), the mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) adjustments of the BCPAP cells had been noticed by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. S8). It was discovered that the MMP orange-red fluorescence depth within the BCPAP cells decreased considerably after 16 µg/mL CA-CDs remedy.
The transwell assay was used to guage the consequences of the CA-CDs on the migration and invasion of the BCPAP cells (Fig. 4B). In contrast with the management group (CA-CDs, 0 µg/mL), the migration and invasion capacity of the BCPAP cells was considerably decreased after remedy with completely different concentrations of the CA-CDs (4 µg/mL, 8 µg/mL, 12 µg/mL and 16 µg/mL). When the focus of the CA-CDs reached 12 and 16 µg/mL, the migration and invasion capacity of the BCPAP cells was inhibited by ~ 65% and ~ 94%, respectively (p < 0.001). It instructed the CA-CDs might considerably and successfully weaken the migration and invasion capacity of the BCPAP cells, which could cut back the opportunity of most cancers cell metastasis and unfold.
(A) After 48 h of remedy with completely different concentrations of the CA-CDs, the fluorescence images of ROS within the BCPAP cells and the corresponding imply fluorescence depth change quantitative column chart. The dimensions bars had been 200 μm. (B) Migration and invasion dyed photographs of the BCPAP cells, and the corresponding statistic diagram of the variety of migrating cells after 48 h remedy with completely different concentrations of the CA-CDs. The dimensions bars had been 500 μm. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 in comparison with Management
Impact of the CA-CDs on the expression of MAPK pathway-related proteins within the BCPAP cells
After 48 h remedy of the BCPAP cells with the CA-CDs (16 µg/mL), transcriptomics evaluation was carried out between the CA-CDs group (CA-CDs 16 µg/mL) and the Management group (CA-CDs, 0 µg/mL). A volcano plot of transcriptome differential gene screening outcomes between the CA-CDs group (n = 5) and the Management group (n = 5) had been plotted (Fig. 5A). In contrast with the Management group, 7596 differential genes had been screened out within the CA-CDs group. Amongst them, 2783 genes had been up-regulated and 4813 genes had been down-regulated. The 2 teams of differential genes (SOS1, KRAS, BRAF, MAPK1, ELK1, GCNT3 and HSPA6) had been randomly chosen for correlation evaluation. It was discovered that the information of the 2 teams (n = 5) had been reproducible and there have been variations between the teams, which might be used for subsequent evaluation (Fig. 5B). For the goal to check the information reliability of the transcriptome, the randomly chosen differential genes SOS1, KRAS, BRAF, MAPK1 and ELK1 in Fig. 5B had been verified by qRT-PCR (Fig. 5D). It may be seen that the down-regulation pattern of those 5 genes was apparent, which was per the pattern of transcriptome sequencing evaluation in Fig. 5B. KEGG enrichment evaluation was carried out on all differential genes, and the highest 20 KEGG pathways with the very best enrichment had been chosen for plotting (Fig. 5C). The signaling pathways with a excessive diploma of differential gene enrichment had been Human papillomavirus an infection, mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway, proteoglycans in most cancers and human immunodeficiency virus 1 an infection.
The WB was used to research the regulatory impact of the CA-CDs on the MAPK classical signaling pathway within the BCPAP cells (Fig. 5E and F). In contrast with the Management group, there was little expression content material change within the BRAF, MEK1 and ERK1/2 proteins within the BCPAP cells, whereas the expression contents of KRAS, p-BRAF, p-MEK1 and p-ERK1/2 proteins had been considerably decreased. It’s speculated that the CA-CDs might concurrently inhibit the proliferation of the BCPAP cells and promote the apoptosis of the BCPAP cells by inhibiting the expression of the continual RAS–RAF–MEK–ERK proteins within the MAPK classical signaling pathway.
Anti-tumor mechanism experiments of the CA-CDs handled the BCPAP cells after 48 h. (A) A volcano plot of transcriptome differential gene screening outcomes of CA-CDs group and Management group (n = 5). Inexperienced dots signify down-regulated genes, and pink dots signify up-regulated genes. (B) Knowledge correlation evaluation warmth map of CA-CDs group and Management group (n = 5). (C) Bubble map of the highest 20 KEGG pathways with the very best differential gene enrichment. (D) The relative mRNA ranges of SOS1, KRAS, BRAF, MAPK1 and ELK1 genes in BCPAP cells in CA-CDs group and Management group, detected by qRT-PCR. (E) WB photographs of MAPK classical pathway-related proteins of BCPAP cells in CA-CDs group and Management group. The Management group was on the left and the CA-CDs group was on the precise. (F) The statistic histogram of relative protein expression
Inhibitory impact of the CA-CDs on poorly differentiated human papillary thyroid tumors in vivo
BCPAP cells had been injected into the subcutaneous pores and skin of BALB/c nude mice, and a xenogeneic tumor-bearing mannequin was established. The tumor-bearing nude mice had been randomly chosen to 3 teams (n = 5) and injected by means of the tail vein: the conventional saline (90 mg/kg, 5 occasions per week) because the Mannequin group; the CA-CDs (2 mg/kg, 5 occasions per week) because the CA-CDs group; the medical anti-thyroid tumor drug cyclophosphamide (CTX, 60 mg/kg, 3 occasions per week) was used because the CTX group. Regular mice had been injected with regular saline (90 mg/kg, 5 occasions per week) within the tail vein because the Management group (n = 5). Regular mice had been injected with the CA-CDs (2 mg/kg, 5 occasions per week) within the tail vein because the Management + CA-CDs group (n = 5). Below the identical feeding situation, the experimental cycle was set 14 days, inside which noticed the indications of the mice. On the 14th day, the subcutaneous tumors of nude mice had been eliminated for detection and evaluation. In contrast with the Mannequin group, the tumor quantity and weight of mice within the CTX group and the CA-CDs group had been considerably decreased (Fig. 6A, B and C). The tumor quantity of mice within the CA-CDs group decreased extra, in contrast with that within the CTX group (Fig. 6C). The outcomes indicated that low-dose CA-CDs had a superb inhibitory impact on human papillary thyroid tumors, and the inhibitory impact was higher than that of the optimistic management CTX.
The physique weight adjustments of mice within the Mannequin group, Management group, CTX group, CA-CDs group, and Management + CA-CDs group had been recorded to guage the security of CA-CDs. The mice within the Management group, Management + CA-CDs group, Mannequin group and CA-CDs group had been in good situation, and their physique weight was steadily rising (Fig. 6D). The mice within the CTX group grew to become malaise after injection with the drug, and their physique weight was clearly decrease than that of the mice in different teams. The physique weight of mice within the Management + CA-CDs group was increased than that within the Management group. This additionally indicated that the CA-CDs had low toxicity and unwanted side effects to organism, and had good organic security. On the 14th day, the foremost organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney) of mice in every group had been collected for histological evaluation to guage pathological variations (Fig. S9). In contrast with the Management group, there was little organ injury and inflammatory injury in the principle organs of the mice within the CA-CDs group and the Management + CA-CDs group. It additional demonstrated that the CA-CDs could have good biocompatibility in vivo.
H&E staining was used to watch the injury of human papillary thyroid tumor tissue in mice in every group (Fig. 6E). H&E staining confirmed that the tumor cells of mice within the Mannequin group had been tightly organized and there have been fewer apoptotic cells. A lot of apoptotic cells appeared within the tumor tissues of mice within the CTX group and the CA-CDs group. The cells had been loosely organized, and the variety of apoptotic cells was considerably increased than that of the Mannequin group. These outcomes indicated that high-dose CTX and low-dose CA-CDs might promote tumor tissue necrosis. Tunel technique is broadly used to detect apoptosis in tissue sections. Tunel staining confirmed that the tumor cells of mice within the Mannequin group had been tightly organized and blue, and apoptotic cells with brownish-yellow nuclei had been nearly absent. The tumor cells of the mice within the CA-CDs group had been loosely organized, the cell quantity was small, and a lot of the cells had been brown. The tumor cells of the mice within the CTX group weren’t a lot completely different from these within the CA-CDs group (Fig. 6E). The expression of markers associated to differentiation and proliferation (CDK4 protein and Ki-67 protein markers) in human papillary thyroid tumors in every group was noticed by immunohistochemistry (IHC) (Fig. 6E). The outcomes confirmed that the CDK4 and Ki-67 had been extremely expressed within the Mannequin group, reasonably expressed within the CTX group, and calmly expressed within the CA-CDs group. The above outcomes instructed that low-dose CA-CDs might promote apoptosis and inhibit cell proliferation in human papillary thyroid tumor tissues in vivo.
Inhibitory impact of the CA-CDs on human papillary thyroid tumors in vivo. (A) Tumor photographs of the mice within the Mannequin group, CTX group and CA-CDs group. (B) Statistic column chart of tumor weight of the mice in Mannequin group, CTX group and CA-CDs group mice on the 14th day. (C) Statistic chart of tumor quantity of the mice in Mannequin group, CTX group and CA-CDs group mice from 1 to 14 days. (D) The calculated statistic chart of physique statistical weight of mice within the Mannequin group, Management group, CTX group, CA-CDs group and Management + CA-CDs group from 1 to 14 days. (E) H&E staining, Tunel staining, and immunohistochemical staining of tumor marker proteins (Ki-67 and CDK4) of mouse tumors in Mannequin group, CTX group and CA-CDs group. The dimensions bars had been 500 μm. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 in comparison with Mannequin