Mass spectrometry is a strong approach that enables scientists to interrupt down and establish the constructing blocks of absolutely anything by measuring the mass of the tiny particles of which one thing is comprised. It has a significant limitation, nevertheless—about 99% of the pattern being measured is often misplaced earlier than evaluation even begins.
This price of loss hampers the expertise’s potential. It reduces accuracy and sensitivity, wastes assets and complicates pattern preparation, which may result in further errors. Which may not be the case for much longer, although.
A analysis workforce from Brown College has developed a brand new technique for transferring the ions that mass spectrometers analyze, dramatically decreasing pattern loss so almost all of it stays intact.
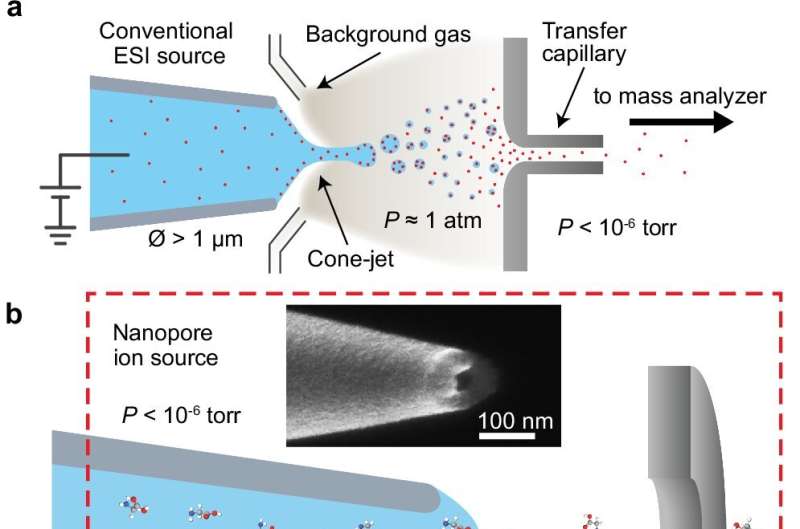
“The traditional approach for producing ions for mass spectrometry, known as electrospray ionization, mainly entails a really sharp needle getting positioned simply in entrance of the mass spectrometer, hitting it with an electrical area that pulls out a sprig of charged droplets that finally dry out to provide naked ions that make it into the mass spectrometer from open air,” mentioned Nicholas Drachman, a physics Ph.D. scholar at Brown who led the work.
“Mainly, it is a course of the place you are actually spraying your pattern in all places to provide these ions and solely get a tiny portion of them into the mass spectrometer’s vacuum for evaluation. Our method skips all of that.”
Known as a nanopore ion supply, the development overcomes a longstanding logjam in science and has the potential to revolutionize mass spectrometry expertise. The Brown workforce describes the novel innovation in Nature Communications.
The secret’s a tiny capillary the researchers developed that has a gap about 30 nanometers throughout—roughly 1,000 occasions smaller than the width of a human hair. For comparability, the traditional needle utilized in electrospray has a gap of about 20 micrometers throughout, which is about 600 occasions greater than the tube developed at Brown.
The brand new nanotube additionally has the distinctive means to switch ions which can be dissolved in water straight into the vacuum of a mass spectrometer, relatively than producing a sprig of droplets that should be dried out to entry the ions.
As well as, standard mass spectrometers sometimes attract a major quantity of gasoline together with the ions throughout the course of, necessitating a number of levels of vacuum pumps to tug within the ions. The brand new breakthrough implies that gasoline will not have to be pumped out, as a result of it will not get sucked in, in line with the researchers.
“Reasonably than place it in entrance of a mass spectrometer and generate this spray of droplets, we simply place it straight into the mass spectrometer, skipping this messy spray, drying and vacuum course of,” Drachman mentioned. “By producing ions within the vacuum straight, it drastically reduces the pumping necessities, which ought to considerably simplify the advanced {hardware} of mass spectrometers.”
The Brown workforce was impressed by nanopore sequencing in DNA and envisions commercializing their concept for widespread use by protein researchers, together with for the long-sought objective of sequencing proteins one amino acid at a time.
“Mass spectrometry is one of the best ways to have a look at proteins, that are made up of amino acids which have all kinds of various chemical and bodily properties, as a result of it may inform them aside by the mass of their ions with excessive certainty,” mentioned Derek Stein, a professor of physics at Brown and creator on the paper.
“Proteomics has not seen the identical advances as genomics within the final 20 years, and so there’s been this starvation for a expertise that may enhance evaluation of proteins. By eliminating that pattern loss drawback, it ought to allow these way more delicate analyses to be attainable, like sequencing the amino acids in a protein molecule one-by-one and in sequential order. That is the blue-sky concept that has motivated our work.”
The workforce spent the previous 10 years engaged on the brand new technique. They began by customized designing their very own mass spectrometer that might home the distinctive ion supply in a vacuum, in contrast to conventional designs the place the ion supply is separate from the machine and sits in open air.
The workforce constructed the important thing element of their switch machine by utilizing a particular machine to warmth a glass tube within the center after which delicately pull it aside to create an especially small opening on the tip invisible to the bare eye.
Trial and error performed a major position within the course of, usually resulting in weeks of frustration as they labored to get every little thing functioning persistently on the tip of the capillary, which is much too tiny to examine by eye.
“There have been some weeks we did not know if we have been cursed by God himself or one thing—issues simply stopped working,” Stein mentioned. “Different weeks, every little thing labored brilliantly.”
The workforce’s persistence paid off. They efficiently demonstrated that ion evaluation with their new switch technique matches detections achieved utilizing conventional strategies however with far much less pattern loss, providing a extra environment friendly and correct strategy to analyze tiny particles.
“We would have liked to persuade individuals within the proteomics area that we will generate the identical type of ions that they’re used to producing by standard electrospray—and that we will do it on this completely different and, we imagine, higher approach,” Drachman mentioned.
The evaluation described within the paper serves as a proof of idea for the strategy. Subsequent, the researchers goal to unlock the complete potential of their nanopore ion supply.
“We have to present that this may enhance the workflow of proteomic analyses,” Drachman mentioned. “We would prefer to take that to the following degree and make it one thing that can enhance the science of researchers all through the sphere.”
Extra data:
Nicholas Drachman et al, Nanopore ion sources ship particular person ions of amino acids and peptides straight into excessive vacuum, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51455-x
Offered by
Brown College
Quotation:
New mass spectrometry expertise may remodel tiny pattern evaluation (2024, September 9)
retrieved 15 September 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-09-mass-spectrometry-technology-tiny-sample.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.