In a world first, College of Waterloo researchers have used 3D imaging expertise to know the effective particulars of microplastics, paving the best way for more practical strategies of plastic waste recycling.
Micro- and nanoplastics, tiny particles of plastic that come from the breakdown of bigger plastic gadgets, have turn out to be an exponentially worsening environmental disaster. On account of their difficulties in safely decomposing, plastic air pollution poses important threats to ecosystems, wildlife and human well being.
Scientists have struggled to know the precise technique of how these micro- and nanoplastics degrade, significantly on the micro- and nanoscale, which has hampered efforts to mitigate their environmental influence. Observing and understanding how the effective particulars of microplastics perform and the way they break down are key to eradicating them from the environment.
In collaboration with the Nationwide Analysis Council (NRC), researchers leveraged 3D imaging expertise along with conventional 2D microscopy, permitting them to watch the degradation of micro- and nanoplastics with unprecedented element.
The examine, “3D imaging photocatalytically degraded micro-and nanoplastics,” was not too long ago printed in Nanotechnology.
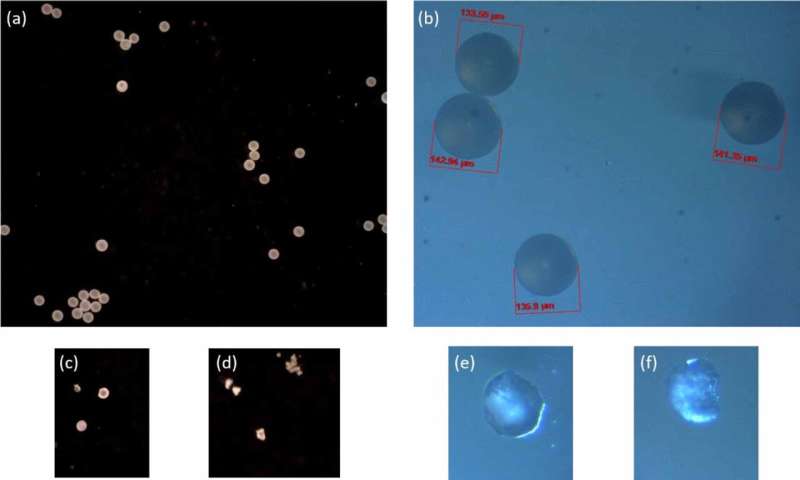
“Most microscope photographs present a two-dimensional view, just like a medical X-ray, which supplies us some data however lacks depth,” mentioned William Anderson, a professor in Waterloo’s Division of Chemical Engineering.
“Nevertheless, 3D imaging is sort of a CT scan, providing way more detailed insights into the construction and degradation of microplastics. This stage of element has been extremely difficult to attain, however it’s essential for understanding what is going on on the floor of micro- and nanoplastics and the way degradation processes work.”
The analysis group used a novel mixture of bodily and organic approaches to acquire their new visible knowledge. They utilized a photocatalytic course of, which handled micro- and nanoplastics with UV mild and a titanium oxide catalyst. Because of this, the group may observe and analyze the degradation at a microscopic stage.
“Utilizing this technique reveals not simply that degradation is going on, however precisely how and the place it is occurring on the floor of micro- and nanoplastics, mentioned chemical engineering professor Boxin Zhao, a College of Waterloo Endowed Chair in Nanotechnology. “This data is essential for growing more practical strategies of breaking down plastics on the micro- and nanoscales.”
Anderson and Zhao, in collaboration with researchers from the Division of Chemical Engineering and the Division of Biology at Waterloo, are growing biocycling strategies the place microplastics may very well be used as a carbon supply for micro organism. These micro organism would ingest microplastics after which excrete an environmentally pleasant biopolymer that may very well be used to create new supplies like plastic baggage or packaging movies.
This examine has broader implications for Waterloo’s analysis group, which is now forming a multidisciplinary plastics biocycling analysis initiative.
The collaboration underscores the significance of bringing collectively completely different fields of experience to deal with advanced environmental challenges. This analysis affords beneficial insights that would pave the best way for more practical strategies of plastic waste recycling and contribute to a round economic system.
Extra data:
Aleksander Cholewinski et al, 3D imaging photocatalytically degraded micro- and nanoplastics, Nanotechnology (2024). DOI: 10.1088/1361-6528/ad5dc5
Offered by
College of Waterloo
Quotation:
3D imaging permits researchers to watch degradation of micro- and nanoplastics with unprecedented element (2024, September 5)
retrieved 8 September 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-09-3d-imaging-degradation-micro-nanoplastics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.