Synthesis and characterization of Cu-MOF
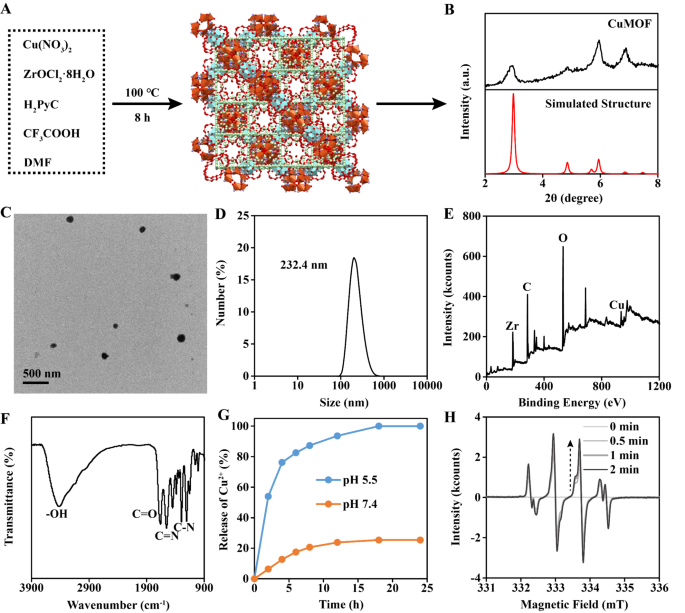
The Cu-MOF was synthesized by means of a broadcast methodology [24]. Briefly, Cu(NO3)2, ZrOCl2·8H2O, CF3COOH, 1 H-pyrazole-4-carboxylic acid (H2PyC) and dimethylformamide (DMF) have been combined. After reacting beneath 100 ℃ for 8 h, the Cu-MOF was obtained (Fig. 2A). The construction of Cu-MOF was MOF-818 as proved by X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Fig. 2B). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and dynamic gentle scattering (DLS) introduced the dimensions of Cu-MOF was about 200 nm (Fig. 2C-D). X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) indicated the existence of Cu atom in Cu-MOF (Fig. 2E). Fourier remodel infrared (FTIR) spectra confirmed the existence of H2PyC skeleton in Cu-MOF (Fig. 2F). Within the Cu2+ launch experiment, it was noticed that Cu2+ nearly utterly launched inside 12 h at pH 5.5, whereas few Cu2+ was detected beneath pH 7.4 (Fig. 2G). Electron spin resonance (ESR) confirmed that Cu-MOF may successfully generate •OH beneath TME (100 µM H2O2 and pH 5.5), which was because of the Fenton response catalyzed by launched Cu2+ (Fig. 2H).
Characterization of Cu-MOF. (A) Synthesis progress of Cu-MOF. (B) XRD evaluation and (C) TEM picture of Cu-MOF. (D) Hydrodynamic dimension of Cu-MOF detected by DLS. (E) XPS evaluation and (F) FTIR spectra of Cu-MOF. (G) Releasing evaluation of Cu2+ from Cu-MOF. (H) The technology of •OH detected by ESR
In vitro tumor therapeutic efficacy of Cu-MOF
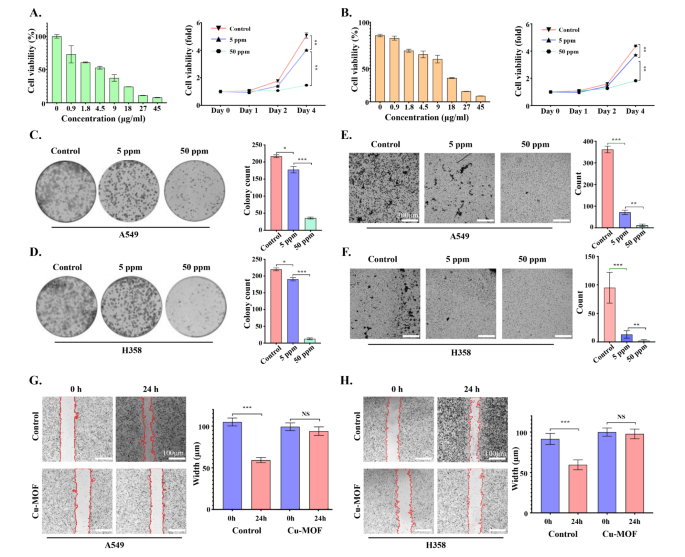
In vitro remedy efficacy of Cu-MOF in A549, SW-1573, NCI-H1975 and NCI-H358 cells was decided by the MTT assay. As proven in Fig. 3A-B and Determine S1-2-3-4, with the rise of Cu-MOF focus gradient, the cell viability of A549, NCI-H358, NCI-H1975 and SW1573 cell traces decreased step by step after 72 h of intervention. As well as, in contrast with the management group, apart from SW1573, low-dose Cu-MOF (5 ppm) may cut back cell viability of the opposite three cell traces (A549, NCI-H1975 and NCI-H358), and the distinction was statistically important. On the similar time, excessive doses of the Cu-MOF (50 ppm) confirmed a better killing efficacy on 4 lung most cancers cell traces on day 4 of the intervention. In concordance, the clone formation of A549 and NCI-H358 cells decreased considerably in low-dose Cu-MOF (5 ppm) group in contrast with management group (Fig. 3C-D). Though low doses of Cu-MOF didn’t considerably inhibit the clonal formation of two cell traces SW-1573 and NCI-H1975 (Determine S1E-F), excessive doses of Cu-MOF had superior anticancer efficacy on all 4 lung most cancers cell traces, and there was a major statistical distinction (Fig. 3C-D and Determine S5–6–7–8). In the meantime, the variety of cell invasions have been considerably decreased within the low-dose group, and a a lot decrease ratio occurred within the high-dose group in comparison with the management group (Fig. 3E-F). Moreover, cells within the management group nearly crawled all around the scratched space after 24 h with a migration price of 43.5% and 34.9% in A549 and H358, respectively, whereas the migration of cells handled with high-dose Cu-MOF was considerably inhibited in each group (Fig. 3G-H). These above mobile outcomes confirmed efficient therapeutic results of Cu-MOF, motivating us to discover its deep anti-tumor mechanism.
Tumor therapeutic efficacy of Cu-MOF nanoparticlesin vitro. Cell viability of A549 (A) and H358 (B) cells after intervention of Cu-MOF with numerous focus gradients at 72 h and numerous therapies with PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF after 4 days. Clonal formation of A549 (C) and H358 (D) cells handled with PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF. Cell invasion conduct and numbers of A549 (E) and H358 (F) cells after completely different therapies have been noticed utilizing the transwell system. Cell migration conduct and width of A549 (G) and H358 (H) cells after completely different therapies have been noticed. Scale bar lengths symbolize 300 μm in Determine E & F and 100 μm in Determine G & H. One-way evaluation of variance (ANOVA) was carried out: ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05
Transcriptomics evaluation of Cu-MOF handled tumor cells
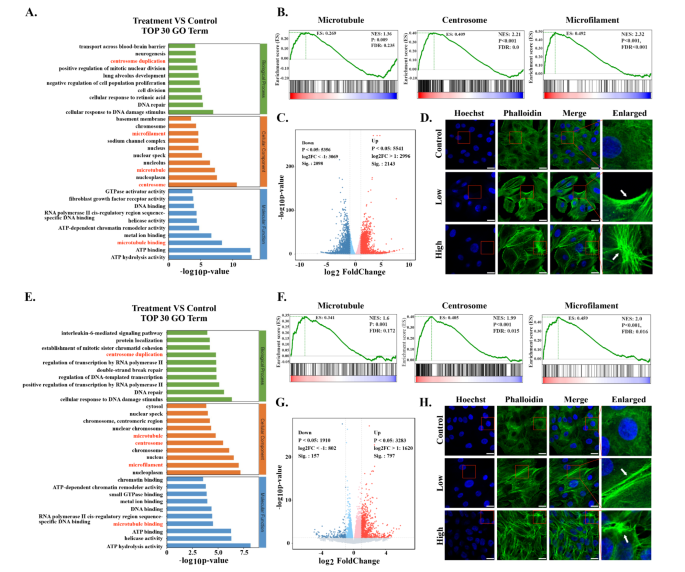
Transcriptomics evaluation was carried out to discover potential anti-tumor mechanisms induced by Cu-MOF. The volcano plot illustrated important adjustments of gene expression between the management group and Cu-MOF group (Fig. 4C-G). GO evaluation demonstrated that the cytoskeletal buildings have been perturbed by Cu-MOF in each A549 and H358 cells clearly (Fig. 4A-E). Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) additional confirmed important variations of gene expression associated to centrosome, microtubule, and microfilament between the Cu-MOF group and management group (Fig. 4B-F). To additional confirm the damaging impact of Cu-MOF on the cytoskeletal buildings of lung most cancers cells, we measured fluorescence of phalloidin and located that high-dose Cu-MOF strongly depolymerized cytoskeletal community (Fig. 4D-H). These outcomes instructed that the cytoskeletal buildings was visibly disassembled by Cu-MOF.
As a dynamic community of intermediate filaments, microtubules, and microfilaments, the cytoskeleton performs an important function in sustaining mobile integrity and regulating numerous mobile processes together with apoptosis [25]. It has been reported that the disruption of the cytoskeleton triggered a cascade of occasions, together with a lower in mitochondrial transmembrane potential, an enhanced launch of cytochrome c, which is important for the activation of caspase-9 and the next initiation of the caspase cascade [26, 27]. These occasions have been discovered to provoke earlier and proceed extra quickly in cells with compromised cytoskeletal buildings. Moreover, the formation of apoptotic our bodies was influenced by the state of the actin system, suggesting that the cytoskeleton not solely impacts the early biochemical occasions of apoptosis but additionally the later morphological adjustments. These outcomes underscores the advanced interaction between the cytoskeleton and apoptotic pathways, demonstrating that cytoskeletal disruption markedly accelerates caspase-3 activation, a pivotal participant within the apoptotic cascade, thereby intensifying apoptotic development [28, 29].
Transcriptome Sequencing Evaluation after Cu-MOF Interventionin vitro. Prime 30 GO time period of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the management and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF teams in each A549 (A) and H358 (E) cells. Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) for microtubules, centrosome and microfilaments associated Cu-MOF remedy in each A549 (B) and H358 (F) cells. Volcano plot primarily based on DEGs between the management and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF teams in each A549 (C) and H358 (G) cells. Confocal pictures of A549 (D) and H358 (H) cell traces after incubation with PBS and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF nanoparticles. Scale bar = 20 μm
Cu-MOF induce tumor cell apoptosis
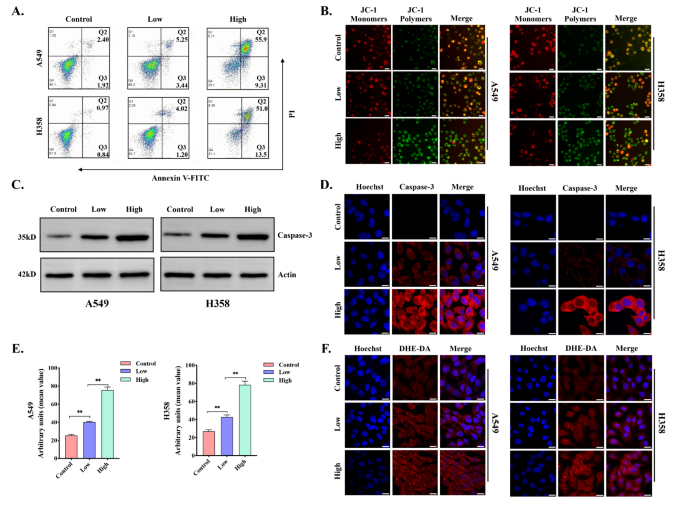
To additional discover whether or not apoptosis occurred in lung most cancers cell traces after Cu-MOF intervention, circulate cytometry Annexin V-FITC and PI staining have been carried out. The info indicated that the proportion of viable A549 and H358 cells have been 94.1% and 97.3% within the management group, respectively. Importantly, the viability of A549 and H358 cells have been additional decreased to 29.1% and 31.1% within the high-dose group (Fig. 5A). On the similar time, the apoptosis price of A549 cell line after intervention ranged from 4.32 to 65.21%, and the information ranged from 1.81 to 64.5% in H358. When A549 and H358 cell traces have been cultured with completely different doses of Cu-MOF for twenty-four h, the proportion of cells in every stage of the cell cycle was detected. In contrast with the management group, the proportion of cells in G2/M section was considerably elevated (A549: from 12.81 to 18.32%; H358: from 12.91 to 19.41%), and the proportion of cells in G0/G1 section was considerably decreased, and this pattern turned increasingly more apparent with the rise of focus (Determine S9–10–11–12).
Caspase-3 is taken into account to be a key government molecule within the early stage of apoptosis, and the activation of Caspase-3 results in mobile dimension discount, cell membrane blistering, chromatin aggregation, and nuclear division, that are typical morphological options of apoptotic cells. Western blot evaluation and immunofluorescence confirmed that the exercise of Caspase-3 elevated considerably with the rise of the intervention focus of Cu-MOF (Fig. 5C-D). As well as, the decline in mitochondrial membrane potential is a signature occasion within the early stage of apoptosis, which may be simply detected by the transition of JC-1 from crimson to inexperienced fluorescence, and our examine additionally confirmed that the mitochondrial membrane potential decreased considerably with the rise of the focus of Cu-MOF (Fig. 5B).
In vitro tumor apoptosis induced by Cu-MOF. (A) Circulation cytometric evaluation of A549 and H358 cells handled with PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF (n = 3, imply ± SD). (B) Mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1) fluorescence pictures of A549 and H358 cells after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF). (C) Western blot evaluation of the expression of casepase-3 in A549 and H358 cells handled with PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF. (D) Casepase-3 fluorescence pictures of A549 and H358 cells after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF). (E) Arbitrary models of ROS fluorescence depth in A549 and H358 cells after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF) (n = 3, imply ± SD). (F) Fluorescence pictures of A549 and H358 cells with ROS produced after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF). Scale bars: 20 μm. One-way evaluation of variance (ANOVA) was carried out: ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), together with the hydroxyl radical (•OH), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), singlet oxygen (O2), and the superoxide radical anion (O2•−), are predominantly produced by the mitochondrial respiratory chain throughout intracellular redox reactions. On condition that tumor cells include greater ranges of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), this microenvironment promotes the Fenton response catalyzed by copper, resulting in the technology of poisonous hydroxyl radicals (•OH). An extreme accumulation of ROS can result in oxidative harm throughout numerous mobile elements, together with nucleic acids, mitochondria, and proteins, probably culminating in cell apoptosis [8]. To additional examine the mechanism by which Cu-MOF disrupts the cytoskeletal construction resulting in apoptosis, we analyzed the degrees of intracellular ROS in A549 and H358 cells by CLSM evaluation (Fig. 5E-F). Because the focus of the Cu-MOF elevated, DHE-DA fluorescence intensities have been prominently enhanced. The high-dose group confirmed the best fluorescence sign (Fig. 5E-F). These outcomes additional confirmed that the Cu-MOF had superior anticancer efficacy, which elevated with the rise of Cu-MOF focus. Beneath the tumor microenvironment, an sufficient quantity of copper ions is launched, which catalyzes the conversion of H2O2 into •OH to trigger harm to mobile elements, notably the cytoskeletal construction. This disruption additional induces G2/M section arrest and triggers the activation of caspase-3, finally resulting in the induction of apoptosis in KRAS mutant NSCLC cells.
Cu-MOF induce tumor cell cuproptosis
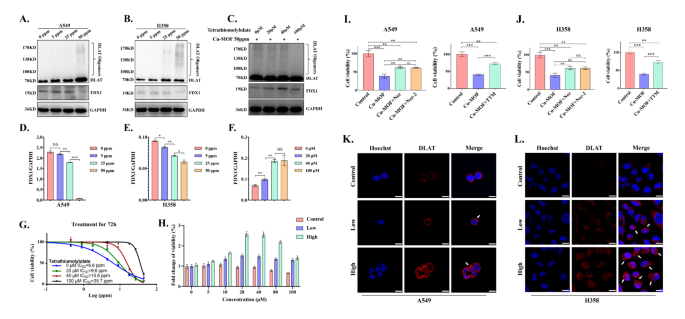
Cuproptosis induced by extra intracellular copper is a novel type of programmed cell loss of life involving lipoylated protein aggregation and subsequent iron-sulfur cluster (Fe-S cluster) protein loss, which depends on mitochondrial respiration [30, 31]. As a mitochondrial lipidated proteins, DLAT is straight certain by copper ions to supply lipidated protein aggregation, which finally promotes proteotoxic stress-induced copper loss of life. Western blotting assay and confocal pictures have been carried out to detect DLAT aggregation. When A549 and H358 cells handled with completely different dose of Cu-MOF, we discovered that the elevated Cu-MOF focus elevated the diploma of DLAT aggregation by protein expression and mitochondrial fluorescence assay (Fig. 6A-B-Ok-L). As well as, Ferredoxin 1 (FDX1) was recognized as the important thing gene related to cuproptosis, which was straight certain to copper ions and result in inhibition of the Fe-S cluster formation perform. Western blot outcomes additionally confirmed that the expression of FDX1 protein decreased step by step with the rise of Cu-MOF focus (Fig. 6A-B-D-E).
To verify that cuproptosis performs a job in Cu-MOF induced cell loss of life, TTM (Tetrathiomolybdate, a copper-chelating agent) was used to judge the impact of copper chelation on the cytotoxicity of Cu-MOF in H358 most cancers cells. The cell viability was measured after mixed remedy with Cu-MOF and TTM, after which was expressed as fold change relative to that of the cells in Cu-MOF intervention alone. As proven in Fig. 6G-H, considerably higher rescuing results, together with cell viability and fold change of viability, have been occurred in Cu-MOF and TTM co-treated cells, in contrast with Cu-MOF intervention alone. In co-culture cell traces, with the rising focus of TTM, the diploma of DLAT aggregation decreased and the expression of FDX1 elevated considerably (Fig. 6C-F), which additionally indicated that cuproptosis was rescued after TTM intervention in Cu-MOF-treated lung most cancers cells.
To additional decide the predominant mode of cell loss of life in antitumor impact of Cu-MOF, we carried out rescue experiments on cells handled with Cu-MOF, using each apoptosis inhibitors together with Necrosulfonamide (i.e., Nec) and Necrostatin-2 racemate (i.e., Nec-2) and cuproptosis inhibitors of Triethylenetetramine (i.e., TTM). Consistent with our earlier findings, Cu-MOF considerably decreased cell viability to 38.5% in A549 cells and 41.1% in H358 cells. Nonetheless, upon the addition of Nec and Nec-2, there was a major enchancment in cell viability for each cell traces, which was elevated to 61.8% for A549 and 61.5% for H358 with Cu-MOF + Nec, and to 61.3% for A549 and 61.2% for H358 with Cu-MOF + Nec-2 (Fig. 6I-J). Furthermore, a comparability between Cu-MOF alone and the mix of Cu-MOF with TTM demonstrated a considerable improve in cell viability from 41.3 to 73.8% within the A549 cell line and from 39.8 to 73.1% within the H358 cell line. Notably, when TTM was added alone, the development in cell viability for each cell traces was considerably higher than that noticed in teams handled with apoptosis inhibitors solely (Fig. 6I-J). This means that cuproptosis is a extra dominant type of cell loss of life induced by Cu-MOF than apoptosis.
In vitro tumor cuproptosis induced by Cu-MOF. Western blot evaluation of the expression of DLAT oligomerization and Fe − S cluster protein in A549 (A) and H358 (B) cells after the indicated therapies. (C) DLAT oligomerization and Fe − S cluster protein expression in H358 cells after co-treated with high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF and cuproptosis inhibitors TTM (0, 20, 40, 100 µM). Ratio of FDX1/GAPDH expression in A549 (D), H358 (E) cells after the indicated therapies. (F) Ratio of FDX1/GAPDH expression in H358 cells after co-treated with high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF and cuproptosis inhibitors TTM (0, 20, 40, 100 µM). (G) Cell viability curve of H358 cells co-treated with high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF and cuproptosis inhibitors TTM (0, 20, 40, 100 µM) 72 h. (H) Fold change of viability of H358 cells co-treated with completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF) and cuproptosis inhibitors TTM (0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 100 µM) 72 h. Cell viability of A549 (I) and H358 (J) cells co-treated with Cu-MOF and apoptosis inhibitors (Necrosulfonamide [Nec] at 10 µM and Necrostatin-2 racemate [Nec-2] at 10 µM) and cuproptosis inhibitors (Triethylenetetramine [TTM] at 30 µM) 72 h. DLAT fluorescence pictures of A549 (Ok) and H358 (L) cells after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (5 ppm), and high-dose (50 ppm) Cu-MOF). White arrows indicated DLAT aggregation. Scale bars: 20 μm. Pupil’s t-test was carried out: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
In vivo the antitumor means of Cu-MOF
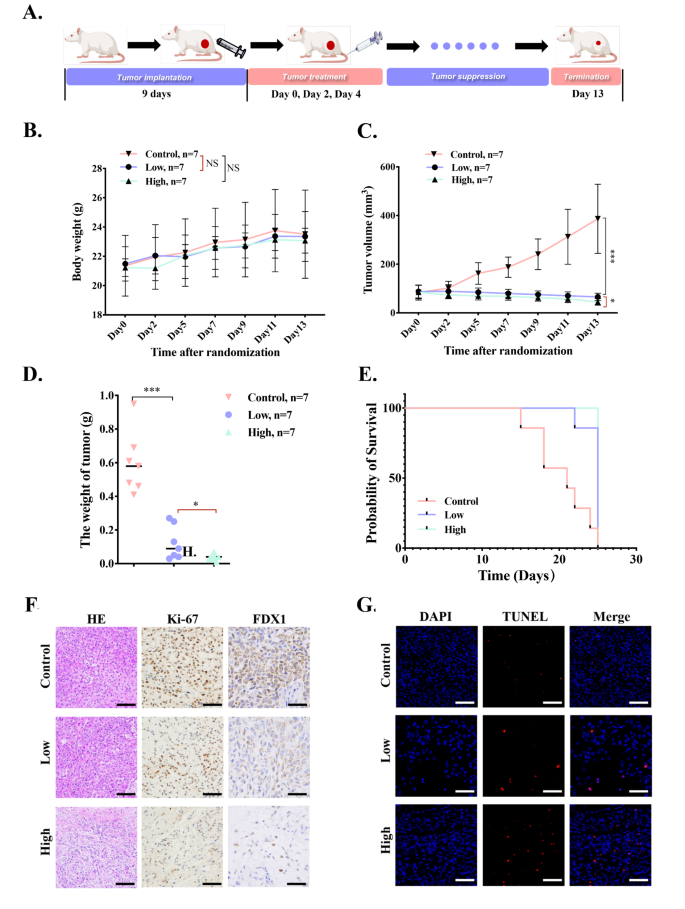
To discover the in vivo anticancer efficacy of Cu-MOF on BALB/c nude mice bearing A549 tumors, we repeatedly monitored the physique weight and tumor quantity of mice for 13 days. The mice have been randomly divided into three teams (n = 7 per group) and intratumorally injected 4 instances on day 0, 2 and 4, respectively, with: (i) PBS, (ii) low-dose Cu-MOF (5 ppm), (iii) high-dose Cu-MOF (50 ppm) (Fig. 7A). Firstly, the physique weight of mice will increase barely and don’t have any important distinction among the many three therapies (Fig. 7B), indicating that Cu-MOF don’t have any system toxicity. As well as, the tumor quantity in management group will increase quickly, which is 4 instances of preliminary quantity (Fig. 7C). In comparison with the management group, low-dose Cu-MOF remedy produced 83.1% inhibition of tumor development, on the similar time, tumor development was inhibited by 88.2% in high-dose Cu-MOF remedy group. Referring to the load adjustments of tumor in three teams, tumor inhibition charges have been calculated to be 82.7% and 88.8% for low-dose and high-dose group, respectively (Fig. 7D). Importantly, the tumors in high-dose Cu-MOF group didn’t considerably improve and even shrink inside therapies. These outcomes instructed that the Cu-MOF produced an environment friendly therapeutic impact. As proven in Determine S17, the tumor-suppressing impact of every group is obvious compared. In response to Kaplan-Meier survival curve, the lifespan of mice in high and low dose Cu-MOF group was considerably longer than that in management group (Fig. 7E), additional evidencing the wonderful antitumor efficacy of Cu-MOF.
To additional study the anti-tumor impact, H&E, and Ki-67 staining have been carried out. The outcomes of H&E staining for necrosis evaluation confirmed that Cu-MOF particularly excessive dose group prompted probably the most extreme harm to the tumors (Fig. 7F). Ki-67 protein, a marker of tumor proliferation, decreased considerably within the high-dose Cu-MOF group (Fig. 7F), indicating that the tumor killing means was enhanced with the rise of dose.
To additional present a extra complete understanding of the cell loss of life mechanisms induced by Cu-MOF in vivo, TUNEL assay and immunohistochemical (IHC) evaluation of FDX1 have been carried out in our animal experiments. The TUNEL assay outcomes indicated a pronounced improve within the sign for apoptosis within the Cu-MOF handled teams when in comparison with the management group, suggesting a major induction of apoptosis (Fig. 7G). Moreover, the IHC evaluation revealed a notable lower within the expression of FDX1, a biomarker indicative of cuproptosis, inside the tumor tissues of the Cu-MOF handled mice (Fig. 7F). This discovering corroborates the in vitro observations and reinforces the function of Cu-MOF in inducing cuproptosis and apoptosis.
This verified that Cu-MOF remedy laid a basis for implementing methods to control cell loss of life to realize higher antitumor remedy outcomes. To determine the biocompatibility of Cu-MOF nanoparticles, histological examination of the most important organs of mice after the intervention confirmed that no important alterations have been noticed (Determine S13). As well as, blood samples have been additionally collected when mice have been sacrificed. The outcomes of blood routine, liver and kidney perform indexes additionally exhibit no overt change in all group (Determine S14). Although white blood cells and lymphocytes are inclined to rise because the drug focus will increase, they’re nonetheless inside the regular vary (the dashed line is the conventional vary) (Determine S14A-E). The outcomes above indicated the excessive biocompatibility and no considerable in vivo toxicity of Cu-MOF.
In vivo the antitumor means of Cu-MOF. (A) In vivo therapeutic schedule of MOF-Cu (n = 7). (B) Physique weight of BALB/c nude mice bearing A549 tumors throughout 13-day therapies (n = 7). (C) Tumor quantity development curves through the 13-day therapeutic interval. (D) The burden of excised tumors on the thirteenth day. (E) Survival curves of tumor-bearing mice with completely different therapies throughout 25 days of monitoring (n = 7). (F) Consultant H&E staining, immunohistochemical staining together with Ki67 and FDX1 pictures of excised tumors amongst three teams after interventions. (G) TUNEL fluorescence pictures after completely different therapies (PBS, low-dose (0.05 mg per mouse), and high-dose (0.1 mg per mouse) Cu-MOF). Scale bars: 20 μm. Pupil’s t-test was carried out: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001
The novel therapeutic technique using Cu-MOF for lung most cancers remedy presents a number of compelling benefits over typical therapies akin to chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiotherapy. Firstly, the focused launch of copper ions within the acidic microenvironment of lysosomes permits for a extra exact assault on most cancers cells, minimizing harm to wholesome tissues. Secondly, Cu-MOF provide a twin mechanism of motion, inducing each apoptosis and cuproptosis, probably offering a stronger therapeutic impact. This strategy is especially promising for KRAS-mutated NSCLC, a subset of sufferers who typically exhibit resistance to immunotherapies and develop resistance to focused therapies inside a 12 months. Moreover, Cu-MOF have demonstrated good biocompatibility and low systemic toxicity in vivo, suggesting a positive security profile. The progressive use of Cu-MOF as a therapeutic agent additionally presents a brand new avenue for overcoming tumor resistance to present therapies. Moreover, the potential for broad applicability to different cancers means that this technique may revolutionize most cancers remedy past the scope of lung most cancers. These advantages spotlight Cu-MOF as a promising candidate for advancing most cancers remedy, warranting additional exploration and improvement.