September 4, 2024
Spear phishing is a well-liked technique of delivering malware to computer systems in massive organizations. It differs from common phishing in that the attackers collect info upfront and personalize the message they ship to encourage the sufferer to carry out an motion that can end in a safety breach. The first targets are both high-level workers with entry to worthwhile info, or workers in departments that work together with a number of recipients. That is very true for HR employees who obtain many emails from strangers which have attachments in a wide range of codecs. That is the assault vector of selection for the menace actors within the case we’re about to debate.
In March 2024, a big Russian firm within the rail freight trade contacted Physician Net. A suspicious e mail with an attachment caught the eye of their info safety division. After attempting to find out the menace posed by the hooked up file, they contacted our specialists. After reviewing the request, our analysts concluded that the corporate had nearly been the sufferer of spear phishing. The purpose of the perpetrators was to assemble system info and launch modular malware on a compromised PC.
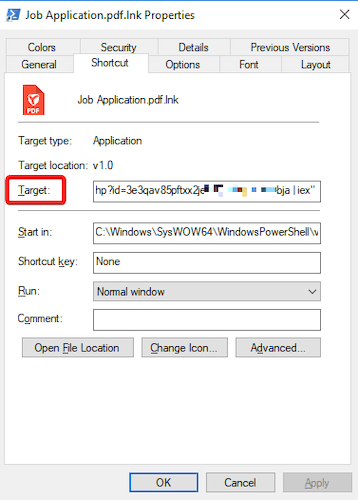
To hold out the assault, the criminals despatched a phishing e mail disguised as a jobseeker’s résumé to the corporate’s e mail handle. Hooked up to the e-mail was an archive purporting to include a PDF file containing a job software. That file had the so-called “double” extension of .pdf.lnk. Hiding malicious objects through the use of double extensions is a typical tactic employed by attackers to idiot their victims. By default, Home windows hides file extensions as a comfort to the person. And when a file has a “double” extension, the system solely hides the final extension. On this case, the sufferer might see the primary extension—.pdf, whereas the .lnk extension was hidden. Furthermore, even when the show of full filenames is enabled, the .lnk extension is at all times hidden by the working system.
The thought of compromising techniques utilizing lnk information shouldn’t be new. Probably the most notable assault occurred in 2010, when uranium enrichment services within the Iranian metropolis of Natanz suffered an unprecedented cyberattack. A worm referred to as Stuxnet attacked the PLCs that managed gasoline centrifuges, spinning them to excessive speeds after which stopping abruptly, destroying their casings. Along with damaging the tools, the worm contaminated greater than 200,000 computer systems in lots of international locations around the globe. The first assault vector was an lnk file that ended up on a USB drive on a company management laptop. To run the trojan horse, the person merely needed to navigate to the folder containing the weaponized lnk file. The assault exploited 4 zero-day vulnerabilities, most notably the CPLINK exploit, which allowed the Stuxnet worm to launch with out person involvement.
Metadata saved in an lnk file
The true .lnk extension is an extension for shortcuts in Home windows. Within the Goal subject, you possibly can specify the trail to any working system object, akin to an executable file, and run it with the required parameters. This assault covertly launched the PowerShell command immediate, which downloaded from the attackers’ web site two malicious scripts, every of which launched its personal payload.
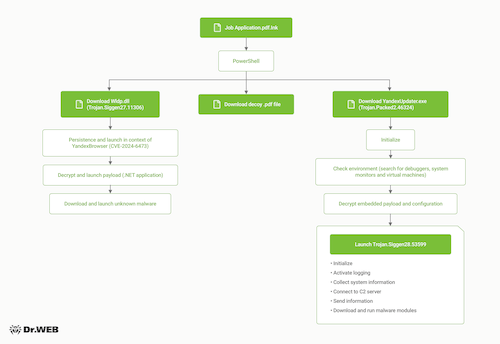
Assault chain
The primary was a decoy PDF and executable file referred to as YandexUpdater.exe, which posed as a part for updating Yandex Browser (the identify of the actual part is service_update.exe). This executable is a malware dropper referred to as Trojan.Packed2.46324, which, after conducting a collection of checks to find out whether or not it’s working in an emulated surroundings and whether or not debugging software program is current, unpacks Trojan.Siggen28.53599 on the compromised system. The latter has distant management capabilities, collects system info and downloads varied malicious modules. Along with these capabilities, the trojan additionally has anti-debugging capabilities. If antivirus, digital machine and debugger processes are detected, the trojan overwrites its file with zeros and deletes it and the folder by which it was saved.
Decoy PDF file
The second payload consisted of a decoy PDF file and Trojan.Siggen27.11306. This trojan is a dynamic library (DLL) with an encrypted payload. A singular function of this trojan is that it exploits the vulnerability of Yandex Browser to DLL Search Order Hijacking. In Home windows, DLL information are libraries that purposes use to retailer capabilities, variables and interface components. When launched, the purposes seek for libraries in a number of knowledge shops in a selected order, so attackers can attempt to “leap the queue” and place a malicious library within the folder the place DLL searches are prioritized.
Simplified DLL search prioritization scheme
This trojan is saved within the hidden %LOCALAPPDATApercentYandexYandexBrowserApplication folder beneath the identify Wldp.dll. That is the listing the place Yandex Browser is put in and the place the browser appears to be like for the libraries it wants at startup. In flip, the reputable Wldp.dll library, whose operate is to make sure the safety of software startup, is an OS system library and is situated within the %WINDIRpercentSystem32 folder. Because the malicious library is situated within the Yandex Browser set up folder, it’s loaded first. On the similar time, it will get all of the permissions of the principle software: it might probably execute instructions and create processes on behalf of the browser, in addition to inherit firewall guidelines for Web entry.
After the browser is launched, the malicious Wldp.dll library decrypts the payload embedded in it. Notice that the decryption is completed twice. The primary time it’s performed utilizing a key generated from the hash of the trail the place the malicious DLL is situated, after which utilizing a worldwide key embedded within the physique of the trojan. The decryption ends in shell code, the execution of which permits attackers to run an software, written within the .NET language, on the compromised system. This executable, in flip, downloads malware from the community. Sadly, on the time of our investigation, the server that the downloader was speaking with was down, and we have been unable to find out what particular trojan was being downloaded on this case.
Thus, we see a multi-vector, multi-stage an infection scheme with two totally different trojans which can be delivered to a compromised system when a file from a phishing e mail is opened. Regardless of the complexity of the implementation, stopping and defending towards such assaults is kind of easy:
- Increase worker consciousness of knowledge safety points (rigorously test hyperlinks and filenames, and don’t open suspicious objects).
- Use software program merchandise that carry out e mail filtering, akin to Dr.Net Mail Safety Suite, to forestall the supply of malicious emails and attachments.
- Set up antivirus software program, akin to Dr.Net Desktop Safety Suite and Dr.Net Server Safety Suite, on all community nodes, which can forestall a harmful file from getting via when customers are engaged on the Web or block suspicious actions on person computer systems if a file was delivered on a USB drive.
- Often apply software program updates that repair program bugs.
Having found this vulnerability in Yandex Browser, we submitted our findings to Yandex. The builders promptly launched an up to date model of Yandex Browser (24.7.1.380) the place this vulnerability (CVE-2024-6473) is fastened.
To make sure the protection of Yandex Browser customers, we have now coordinated the discharge date of this text with browser builders to permit customers to improve to a patched model of Yandex Browser earlier than the main points of this assault are made public.