Quite a lot of quickly digitized essential infrastructure sectors in India — from finance to authorities techniques and from manufacturing to healthcare — now are going through elevated cyberattacks and cyber threats.
Contemplate this: A hacking group in April of this 12 months leaked 7.5 million information containing private data stolen from India’s main producer of wi-fi audio and wearable units boat. Most lately, the Reserve Financial institution of India — the nation’s central financial institution — referred to as out elevated digitization as a possible danger for the nation’s monetary infrastructure. Cyber incidents towards finance and dealt with by the nationwide CERT crew jumped to some 16 million incidents in 2023, up from 53,000 in 2017, in line with a latest report by RBI.
The overwhelming majority of banks and most non-bank monetary corporations (NBFCs) think about cybersecurity to be a major problem to their skill to transition to digital applied sciences, in line with the financial institution’s report. “Digitalisation might pose monetary stability considerations owing to cybersecurity threats, information breaches, and the pace at which data and rumours can circulation by the system,” the RBI acknowledged in its report. “Cyber fraudsters are more and more focusing on monetary establishments as a substitute of finish customers globally.”
India’s monetary sector will not be alone. Public sector and authorities techniques have seen a dramatic improve in cyberattacks, with most set up seeing cyberattacks develop by at the least half.
Earlier this 12 months, a hacking group focused authorities companies and power corporations with a Trojan dubbed HackBrowserData. In the meantime, Pakistan, and China incessantly goal Indian organizations in cyber operations, equivalent to latest Cosmic Leopard operations within the area.
Total, 83% of organizations in India reported at the least one cybersecurity incident within the final 12 months, inserting the nation at No. 4, behind Vietnam (94%), New Zealand (90%), and Hong Kong (86%) in rankings for the Asia-Pacific area, in line with a Cloudflare report.
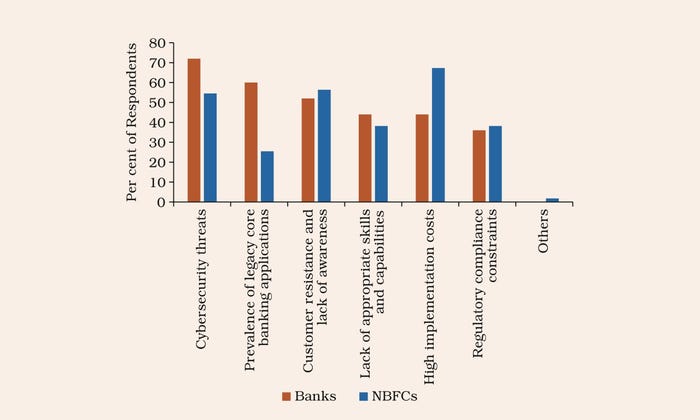
The first challenges hobbling the adoption of digital applied sciences. Supply: RBI employees estimates based mostly on survey responses from 25 banks and 55 NBFCs.
On a worldwide degree, the nation is the fifth most breached nation and must focus extra on cybersecurity, says Partha Gopalakrishnan, founding father of PG Advisors, an AI and digital transformation consultancy.
“India may benefit from much more sturdy cybersecurity measures,” he says. “The principle piece of laws governing cybercrime is the Data Know-how Act 2000 … now, 24 years previous and outdated.”
Prime Worries: Cloud and Units
Indian organizations are most involved about cloud-related threats (52%), assaults on related units (45%), hack and leak operations (36%), and software program provide chain compromises (35%), in line with PwC’s The C-Suite Playbook report for India.
The adoption of rising applied sciences equivalent to AI and cloud and the concentrate on innovation and distant working has pushed digital transformations, thus boosting corporations’ want for extra safety defenses, in line with Manu Dwivedi, accomplice and chief for cybersecurity at consultancy PwC India.
“AI-enabled phishing and aggressive social engineering have elevated ransomware to the highest concern,” he says. “Whereas cloud-related threats are regarding, better interconnectivity between IT and OT environments and elevated utilization of open-source parts in software program are rising the obtainable menace floor for attackers to take advantage of.”
Indian organizations additionally must harden their techniques towards insider threats, which requires a mixture of enterprise technique, tradition, coaching, and governance processes, Dwivedi says.
AI for Good, AI for Evil
The rising demand for AI has additionally formed the menace panorama within the nation and menace actors have already began experimenting with completely different AI fashions and methods, says PwC India’s Dwivedi.
“Menace actors are anticipated to make use of AI to generate personalized and polymorphic malware based mostly on system exploits, which escapes detection from signature-based and conventional detection strategies,” he says. “Going ahead, it might be tougher to find out how all kinds of menace actors are misusing GenAI.”
As well as, AI fashions could possibly be harnessed to assist malicious actors change into extra environment friendly and productive, says PG Advisors’ Gopalakrishnan.
“Using AI in cyberattacks is exacerbated by the AI abilities hole in India, making coaching within the areas of each AI and cybersecurity an absolute precedence inside Indian companies,” he says, including: “AI will place better energy within the arms of hackers sooner or later, making it accessible for individuals who may in any other case lack the abilities and capabilities to launch cyberattacks.”