Researchers on the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have been bettering the decision of a course of generally known as photolithography. They hope to make use of their method to assist advance the miniaturization of laptop chips.
Miniaturizing laptop chips is likely one of the keys to the digital revolution. It permits computer systems to turn into ever smaller and, on the similar time, extra highly effective. This in flip is a prerequisite for developments akin to autonomous driving, synthetic intelligence and the 5G commonplace for cellular communications. Now a analysis staff led by Iason Giannopoulos, Yasin Ekinci and Dimitrios Kazazis from the Laboratory of X-ray Nanoscience and Applied sciences on the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has devised a way for creating even denser circuit patterns.
The present state-of-the-art microchips have conductive tracks separated by twelve nanometers, i.e. about 6000 instances thinner than a human hair. The researchers, in contrast, have managed to provide tracks with a separation of simply 5 nanometers. In consequence, circuits could be designed rather more compactly than earlier than.
“Our work showcases the patterning potential of sunshine. This can be a vital step ahead for each trade and analysis,” explains Giannopoulos.
Microchips are produced like the images on a cinema display
As not too long ago as 1970, there was solely room for round 1000 transistors on a microchip. Right this moment, an space barely bigger than the tip of a finger can maintain about 60 billion parts. These parts are manufactured utilizing a course of known as photolithography: a skinny slice of silicon, the wafer, is coated with a light-sensitive layer, the photoresist.
It’s then uncovered to a sample of sunshine comparable to the blueprint for the microchip, which alters the chemical properties of the photoresist, making it both soluble or insoluble to sure chemical options. Subsequent therapy removes the uncovered (optimistic course of) or unexposed (destructive course of) areas. In the long run, conductive tracks are left behind on the wafer forming the specified wiring sample.
The kind of gentle used is essential for miniaturization and for making microchips increasingly more compact. The legal guidelines of physics dictate that the smaller the wavelength of the sunshine used, the extra carefully the constructions within the picture could be packed. For a very long time, the trade used deep ultraviolet gentle (DUV). This laser gentle has a wavelength of 193 nanometers. By comparability, the vary of blue gentle seen to the human eye ends round 400 nanometers.
Since 2019, producers have been utilizing “excessive ultraviolet gentle” (EUV) with a wavelength of 13.5 nanometers in mass manufacturing, greater than ten instances shorter than earlier than. This makes it potential to print even finer constructions, down to 10 nanometers and fewer. At PSI, researchers use radiation from the Swiss Mild Supply SLS for his or her investigations, tuned to 13.5 nanometers in accordance with the trade commonplace.
Photon-based lithography can obtain very excessive decision
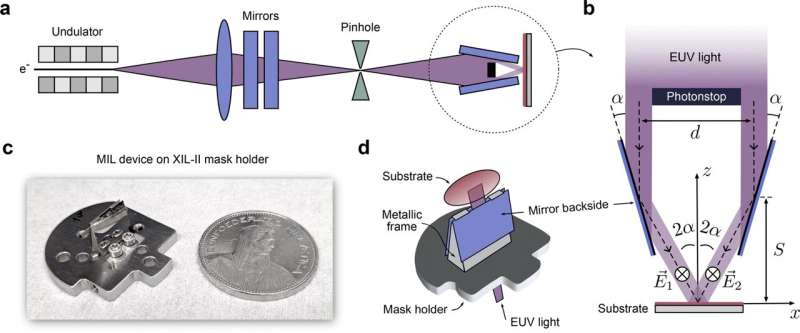
Nevertheless, the PSI researchers prolonged typical EUV lithography by exposing the pattern not directly relatively than straight. In EUV mirror interference lithography (MIL), two mutually coherent beams are mirrored onto the wafer by two an identical mirrors. The beams then create an interference sample whose interval is dependent upon each the angle of incidence and the wavelength of the sunshine.
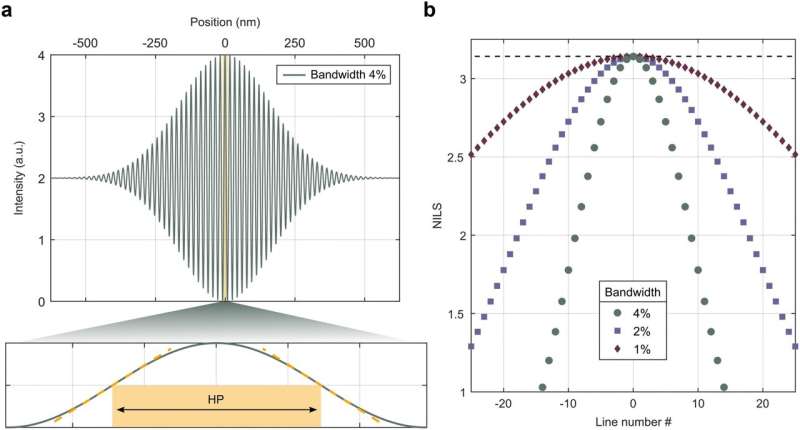
The group was capable of obtain resolutions, i.e. monitor separations, of 5 nanometers—in a single publicity. Considered beneath an electron microscope, the conductive tracks had been discovered to have excessive distinction and sharp edges.
Kazazis notes, “Our outcomes present that EUV lithography can produce extraordinarily excessive resolutions, indicating that there aren’t any elementary limitations but. That is actually thrilling because it extends the horizon of what we deem as potential and may open up new avenues for analysis within the area of EUV lithography and photoresist supplies.”
A brand new EUVL software from the top of 2025
For the time being, this strategy is just not attention-grabbing for industrial chip manufacturing, as a result of it is extremely sluggish in comparison with industrial requirements and may produce solely easy and periodic constructions relatively than a chip design. Nevertheless, it provides a way for the early growth of photoresists wanted for future chip manufacturing with a decision that’s not potential within the trade.
The staff plans to proceed their analysis utilizing a brand new EUV software on the SLS, anticipated by the top of 2025. The brand new software coupled with the SLS 2.0, which is at present going by means of an improve, will present a lot enhanced efficiency and capabilities.
Extra data:
Iason Giannopoulos et al, Excessive ultraviolet lithography reaches 5 nm decision, Nanoscale (2024). DOI: 10.1039/D4NR01332H
Offered by
Paul Scherrer Institute
Quotation:
Photolithography analysis reveals laptop chips have the potential to turn into even smaller (2024, August 13)
retrieved 15 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-photolithography-chips-potential-smaller.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.