A fancy interaction of energetics and dynamics governs the habits of nanocrystals in resolution. These dynamics are often interpreted by way of the speculation developed by Derjaguin, Landau, Verwey, and Overbeek (DVLO), and understanding these forces is especially vital for controlling oriented attachment (OA), the place particular person nanocrystals fuse collectively in particular alignments.
In a new examine printed in ACS Nano, researchers explored the consequences of forces not accounted for in DLVO idea on a zinc oxide (ZnO) mannequin system present process OA. They discovered that the driving forces behind the attachment are dipole–dipole forces that aren’t thought of in DLVO idea.
The dipole forces result in quicker attachment in much less polar options, validated by calculations that account for non-DLVO forces. The researchers additionally confirmed that the brief vary, repulsive forces that gradual attachment rely on the character of the solvent, notably its molecular packing and intermolecular interactions.
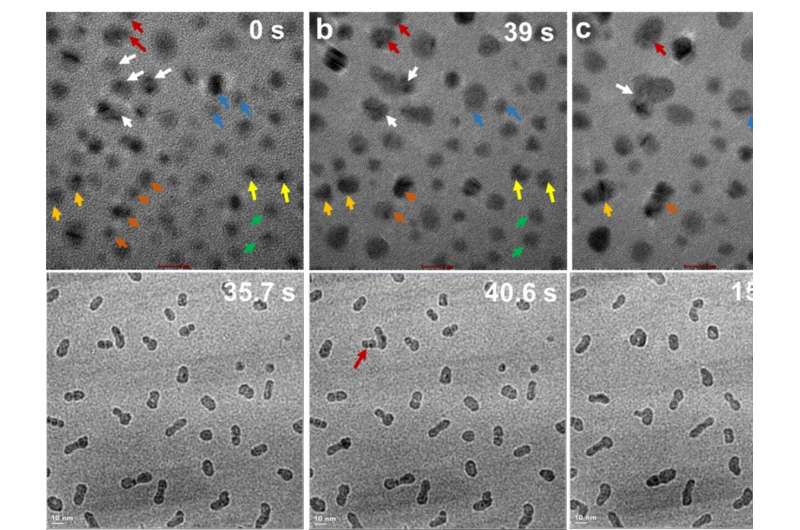
Researchers explored the non-DLVO forces that regulate the dynamics and outcomes of particle aggregation, coalignment, and attachment in a ZnO mannequin system. They investigated the impact of dipole–dipole interactions on the long-range forces and torques that drive particle method and alignment by combining in situ transmission electron microscopy observations of OA occasions with Langevin dynamics simulations utilizing a variety of solvents.
Evaluating the magnitude of those forces to the electrostatic and van der Waals forces calculated utilizing DLVO idea confirmed that the non-DLVO forces dominate and supply a rationale for the discrepancies noticed within the totally different solvents.
Additionally they investigated the short-range repulsive forces arising from the solvent construction close to the ZnO floor utilizing 3D atomic power microscopy. The solvation power is stronger in water in comparison with ethanol and methanol because of the stronger hydrogen bonding and denser packing of water molecules on the interface.
These outcomes spotlight the significance of resolving and quantifying non-DLVO forces in establishing a normal framework for understanding and predicting supplies synthesis through particle aggregation and attachment.
The researchers have created a formidable array of nanomaterials with distinctive properties equivalent to colloidal crystals, mesocrystals, extremely branched nanowires, and adaptive supplies that reply reversibly to exterior stimuli.
Persevering with to advance the sector and develop a predictive understanding of particle aggregation and attachment habits requires shifting past conventional colloidal theories, equivalent to DLVO. Figuring out the totally different forces at play in OA will allow researchers to create situations that produce the precise remaining nanomaterial buildings wanted for purposes.
Extra data:
Lili Liu et al, Impact of Solvent Composition on Non-DLVO Forces and Oriented Attachment of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles, ACS Nano (2024). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.4c01797
Offered by
Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory
Quotation:
Understanding the forces that regulate crystallization by particle attachment (2024, August 6)
retrieved 12 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-crystallization-particle.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.