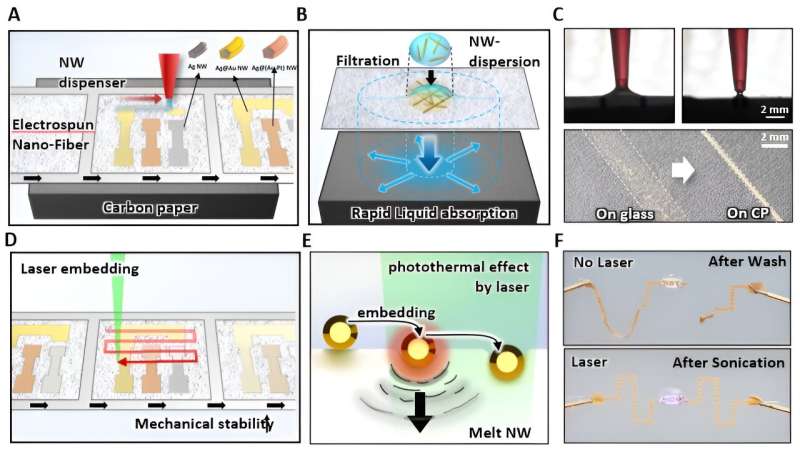
Versatile digital units primarily based on electrospun nanofiber membranes (ENM) are attracting important consideration on account of their excessive biocompatibility and wonderful mechanical efficiency. Nevertheless, patterning conductive supplies on fiber substrates usually requires costly vacuum gear or extra processes to create separate masks.
To deal with this, a collaborative analysis group led by Professor Seung Hwan Ko of the Division of Mechanical Engineering at Seoul Nationwide College and Professor C-Yoon Kim of Konkuk College developed a system that induces environment friendly fluid move utilizing capillary motion by putting a carbon paper help below the nanofiber membrane, enabling the filtration course of with out the necessity for vacuum gear.
The analysis was revealed in Superior Useful Supplies on Could 29.
This method enhances mechanical stability by strongly bonding nanowires and substrates by means of the photothermal results of lasers through the post-processing stage. As well as, the system demonstrated that circuits remained steady even below sturdy ultrasonic remedy and that the patterns on the substrate remained intact when manually pulled.
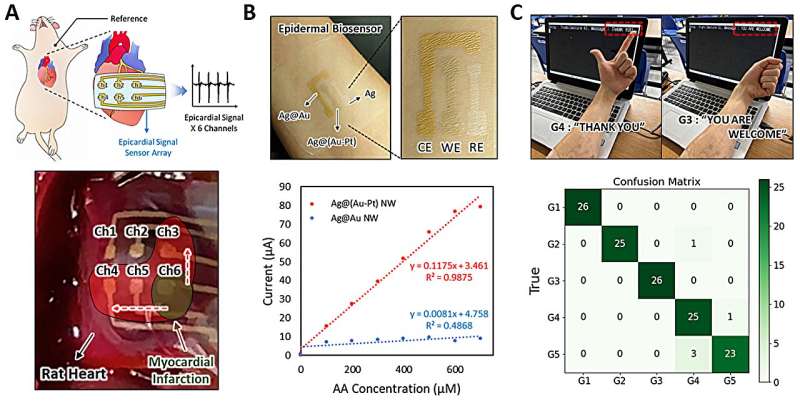
The group validated the strengths of their developed course of system and outcomes by means of numerous functions, together with an in vivo epicardial sign recording ECG electrode, an epidermal electrochemical biosensor, and customised epidermal electromyography (EMG)-based human–machine interface (HMI).
The potential of the electrospun nanofiber membrane (ENM)-based smooth electronics in epidermal bioelectronics has gained enormous consideration with their conformal compatibility with the human physique and related efficiency enhancements.
Nevertheless, patterning conductive supplies on fiber substrates usually requires costly vacuum gear or extra processes to create separate masks.
The analysis group developed a system that permits the filtration course of with out the necessity for expensive vacuum gear by putting a carbon paper help below the nanofiber membrane, inducing environment friendly fluid move by means of capillary motion.
Utilizing this technique, the nanowires and substrates might be strongly bonded by means of the photothermal results of lasers through the post-processing stage, enhancing mechanical stability. The system additionally demonstrated that circuits remained steady below sturdy ultrasonic remedy and that the patterns on the substrate remained intact when manually pulled.
The analysis group validated the strengths of their developed course of system and outcomes by means of numerous functions, together with an in vivo epicardial sign recording ECG electrode, an epidermal electrochemical biosensor, and customised epidermal electromyography (EMG)-based human–machine interface (HMI).
Moreover, this analysis has opened up prospects for effectively fabricating digital units with excessive stretchability, breathability, and conductivity, demonstrating potential functions in numerous well being care and medical fields.
Extra info:
Hyeokjun Yoon et al, Adaptive Epidermal Bioelectronics by Extremely Breathable and Stretchable Steel Nanowire Bioelectrodes on Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane, Superior Useful Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202313504
Supplied by
Seoul Nationwide College School of Engineering
Quotation:
New system enhances mechanical stability of nanofiber-based bioelectrodes (2024, August 7)
retrieved 7 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-mechanical-stability-nanofiber-based-bioelectrodes.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.