Synthesis and characterization of CDs
As proven in Fig. 1A and Determine S1, the shaped CD1/4 with the perfect dissolving impact was spherical in form with common diameter of two.48 ± 0.41 nm and properly dispersed from one another. After lyophilization, CD1/4 was re-dissolved in distilled water. Determine S1 additionally confirmed the particle dimension was nonetheless comparatively small (2.62 ± 0.56 nm), which indicated good redispersion of CD1/4. CD0, CD1/9 and CD1/4 had comparatively excessive absorption round 340 nm, which could possibly be attributed to the formation of defect floor states induced by the N heteroatoms (Fig. 1B) [25]. Nevertheless, this peak sharply decreased in CD1/2, CD3/4 and CD1, indicating discount of nitrogen-related defect floor states. The fluorescence spectrum revealed each fluorescence depth and peak place of CD1/4 had been depending on the excitation wavelength (Determine S2). The FTIR spectra present the attribute peaks of CDs (Fig. 1C). The height at 1534 cm− 1 in lysine, CD0, CD1/9 and CD1/4 could possibly be attributed to amino group (NH2) [26]. This recommended amino teams of lysine had been efficiently integrated into these CDs. As for CD1/9, CD1/4, CD1/2, CD3/4, CD1 and oxalic acid, all of them had peak round 1697 cm− 1 (C = O of oxalic acid) [27]. This indicated incorporation of purposeful teams of oxalic acid into these CDs. CD0, CD1/9, CD1/4 and CD1/2 confirmed a particular attribute peak at 1579 cm− 1, which could possibly be assigned to amide II vibration [28].
The XPS spectra revealed three predominant peaks at 285.9, 400.1 and 531.3 eV, which corresponded to binding energies of C 1s, N 1s and O 1s respectively (Fig. 2A-F). CD0, CD1/9, CD1/4, CD1/2 and CD3/4 contained the identical components, apart from CD1. There was no N-compound in staring supplies of CD1, which triggered absence of nitrogen. Excessive decision of the C 1s spectrum could possibly be divided into 4 binding power subpeaks (Fig. 2G-L), which included 284.5 eV (C = C/C-C), 285.9 eV (C–N/C-O), 287.9 eV (C = O) and 288.7 eV (O = C-O/O = C-N), respectively [28,29,30,31]. From the spectra, it could possibly be seen that the C = C/C-C part had probably the most intense peak amongst the entire deconvoluted peaks, indicating that C = C/C-C was the principle C bonding configuration of CDs. The height at 288.7 eV elevated from 3.73 to 22.43% with the rising ratio of oxalic acid in beginning supplies (Desk S2). This could possibly be attributed to carboxylation by oxalic acid and/or conjugation of oxalic acid to amino teams by amide bonds [31]. The N 1s spectrum (Fig. 2M-Q) could be de-convoluted into two peaks at 400.8 and 399.2 eV, similar to the N-(C)3 and N-H, respectively [30, 32]. The contents of N-H in CD0, CD1/9 and CD1/4 had been comparatively excessive, whereas its contents in CD1/2 and CD3/4 had been fairly low (Desk S3). This indicated practically the entire N ingredient in lysine was transformed into N-(C)3 when excessive quantities of oxalic acid had been added.
When low quantities of oxalic acid had been added in beginning supplies, the yields of CD0, CD1/9 and CD1/4 had been above 92% (Fig. 2R). Because the oxalic acid content material continued to extend, the yield decreased sharply in CD1/2, CD3/4 and CD1. This reducing could possibly be attributed to decarboxylation response of oxalate ester [31]. Combining the outcomes of FTIR, XPS and manufacturing yields, it may be inferred that oxalic acid was conjugated on the floor of CDs by amide bond in CD1/9 and CD1/4, by ester bond in CD3/4 and CD1, by amide and ester bonds in CD1/2.
Gel-sol transition of various metal-alginate hydrogels
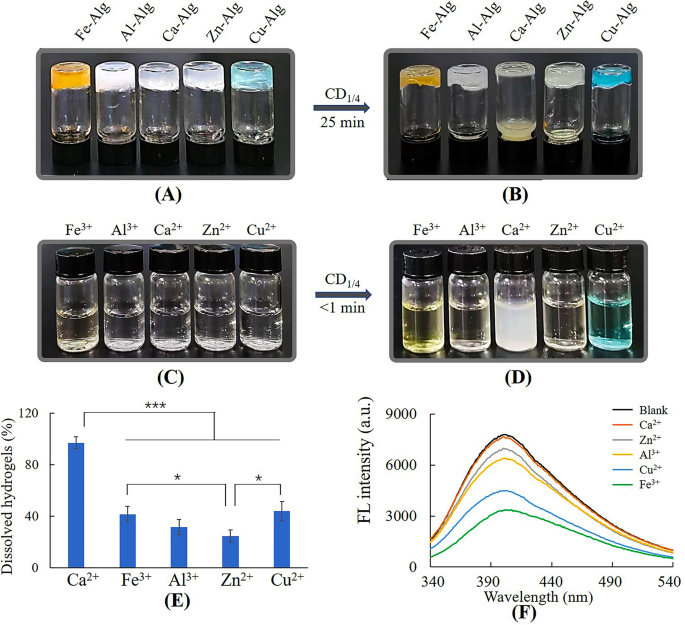
Dissolution of metal-alginate hydrogels by CD1/4. (A) Steel-alginate hydrogels, (B) metal-alginate hydrogels dissolved by 50 mg/mL CD1/4, (C) 2.5 mL of three mM steel ion answer, (D) steel ion answer added with CD1/4 (0.8 mL, 50 mg/mL), (E) the ratio of dissolved hydrogels, (F) fluorescence depth of 0.48 mg/mL CD1/4 with 0.1 mM steel ions
Ca-hydrogel was completely dissolved by CD1/4 inside 25 min, nonetheless, different metal-hydrogels had been solely partially dissolved (Fig. 3A, B and E). Determine 3C and D confirmed solely Ca2+ triggered precipitation after reacting with CD1/4, suggesting the motion mode of Ca2+ differed from different steel ions. Fluorescence spectrum (Fig. 3F) revealed reducing fluorescence depth of CD1/4 after incubating with steel ions apart from Ca2+. In line with earlier stories, Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe3+ and Al3+ are likely to type steel complexes with purposeful teams comparable to amino and carboxylic teams [33,34,35,36], and the static quenching was resulting from formation of non-fluorescent complexes between CD1/4 and these steel ions [29, 37]. The dissolution of those metal-alginate hydrogels could possibly be attributed to the aggressive complexation of CDs with Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe3+ or Al3+ [18]. As for Ca2+, it’s a lot tougher to type steel complexes because of the lack of most well-liked geometrical coordination and coordination numbers, ensuing from its giant ionic radii and digital configuration [38]. Thus, gel-sol transition mechanism of Ca-alginate hydrogel can’t be attributed to aggressive complexation, however could also be associated to formation of white calcium precipitations. The main points had been investigated within the following research.
Impact of amino teams of CDs on gel-sol transition
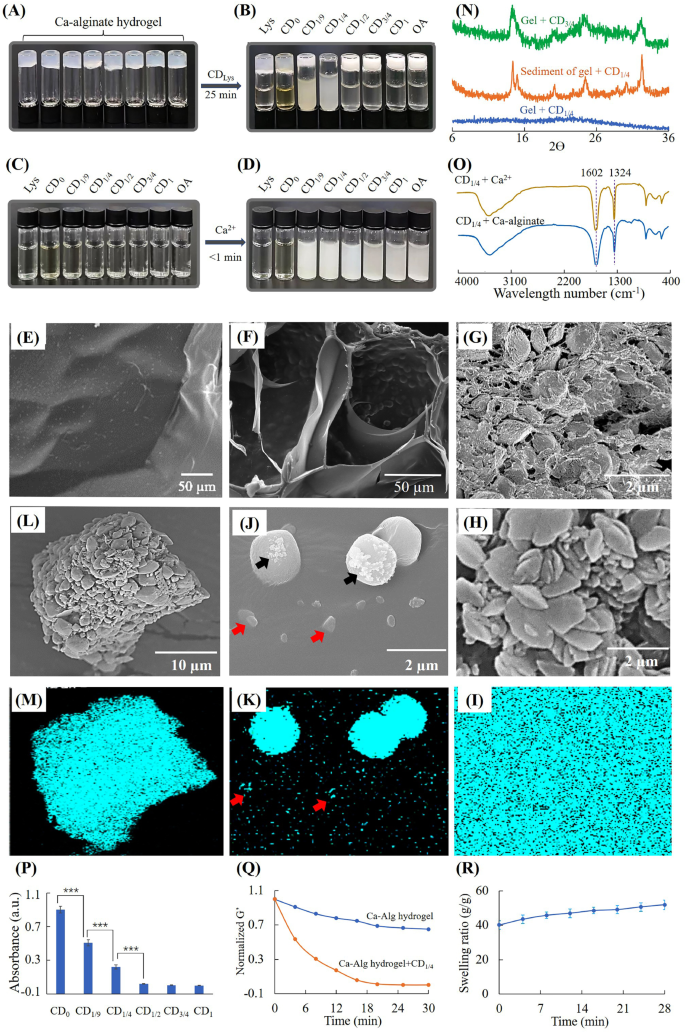
Dissolution of Ca-alginate hydrogel by CDlys. (A) Ca-alginate hydrogel, (B) Ca-alginate hydrogel incubated with 18 mg/mL CDLys, (C) 18 mg/mL CDlys, (D) CDLys added with Ca2+ (remaining focus 3mM), (E) floor morphology of Ca-alginate hydrogel, (F) cross part morphology of Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD1/4 for 15 min, (G) cross part morphology of Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD3/4 for 15 min, (H) morphology and (I) EDS mapping of floor of Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD3/4 for 15 min, (J) morphology and (Okay) EDS mapping of floor of Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD1/4 for 15 min, (L) morphology and (M) EDS mapping of centrifugal precipitation of Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD1/4, (N) XRD spectra, (O) FTIR of calcium precipitations, (P) absorption of CDlys options from ninhydrin exams, (Q) rheological evaluation and (R) swelling of hydrogel throughout degradation by CD1/4 options
Determine 4A-D confirmed that CD1/9 and CD1/4 aqueous options might produce precipitates with Ca2+ and dissolve Ca-alginate hydrogels. CD1/2, CD3/4 and CD1 aqueous options might produce precipitates with Ca2+, however can’t dissolve Ca-alginate hydrogels. When the mass fraction of OA in beginning supplies was ≤ 1/4, the dissolving ratio of CDLys elevated with the rising of OA content material. When the mass fraction of OA was > 1/4, CDLys misplaced their capacity to dissolve Ca-alginate hydrogels. To make clear the variations between dissolved hydrogel and undissolved hydrogel, SEM and XRD had been used to analyze the hydrogels and precipitations. CD1/4 was chosen because the analysis mannequin because of the fastest-dissolving fee, and CD3/4 with none dissolution capacity was used as a comparability. It was noticed by SEM that Ca-alginate hydrogel with none remedy had clean floor buildings (Fig. 4E). After treating with CD3/4 for 15 min, the hydrogel had a really coarse floor constituting of numerous microparticles (Fig. 4G and H). EDS mapping in Fig. 4I demonstrated Ca-alginate hydrogel handled with CD3/4 was totally coated with calcium. XRD spectra in Fig. 4N confirmed attribute peaks at 14.9 and 24.5, which had been the identical to calcium oxalate crystals [39]. These outcomes indicated mineralization of CD3/4 into Ca-alginate hydrogels.
After treating with CD1/4 for 15 min, some clusters with totally different sizes had been depositing on remaining hydrogels (Fig. 4F and J). EDS mapping of calcium revealed low enrichment of calcium on small clusters (pink arrows) and excessive enrichment of calcium on giant clusters (Fig. 4J and Okay). Irregular formed crystals (black arrows) additionally could possibly be seen on a part of giant clusters, which recommended the incidence of mineralization. In an effort to additional examine the destiny of calcium crystals, the suspension after gel-sol transition was centrifugated and separated. Determine 4L and M confirmed EDS map of calcium was completely matched with centrifugal precipitations. XRD spectra of centrifugal precipitations confirmed the identical peaks as calcium oxalate crystals [39], whereas remaining hydrogel had no such attribute peaks. It could possibly be inferred that calcium crystals had been lastly launch to surrounding options.
In an effort to examine whether or not alginate participated in mineralization of CD1/4, the suspension after gel-sol transition was separated by centrifugation and measured by FTIR. As proven in Fig. 4O, the spectrum of sediment separated from hydrogel suspension was the identical as that of sediment generated by CD1/4 and Ca2+. Each of them had peaks at 1602 and 1324 cm− 1, which could possibly be attributed to amide II vibration and C-O stretching vibration of calcium precipitation, respectively [40]. Determine S3 confirmed the spectrum of pure SA was just like that of supernatant separated from the dissolved Ca-alginate hydrogel. Each of them had peaks at 1613, 1413 and 1031 cm− 1, which had been assigned to antisymmetric COO− stretch, symmetric COO− stretch and antisymmetric C-O-C stretch of SA, respectively [41]. The height at 1525 could possibly be assigned to unreacted amino teams in CD1/4. Thus, it could possibly be inferred that alginate didn’t contain in formation of calcium precipitation and was launched to surrounding answer.
As major amine teams have excessive binding capability to carboxyl teams, the quantity of major amine teams on CDs was measured by the ninhydrin response. Determine 4P confirmed the quantities of major amine teams diminished quickly with the rising of oxalic acid. When the content material of oxalic acid in beginning supplies elevated to 50%, there was barely no major amine group on the floor of CDLys. Determine 4Q confirmed the storage modulus of hydrogel decreased with time, indicating the hydrogel dissolved progressively. Determine 4R confirmed the Ca-alginate hydrogel swelled throughout dissolution of by CD1/4. The swelling of hydrogels could possibly be attributed to 2 purpose; ① displacement of cross-linking Ca2+ by amino teams, ② seize of Ca2+ by CDs [42]. These render the Ca-alginate hydrogel construction unfastened and soluble.
Impact of various N-groups on floor of CDs on gel-sol transition
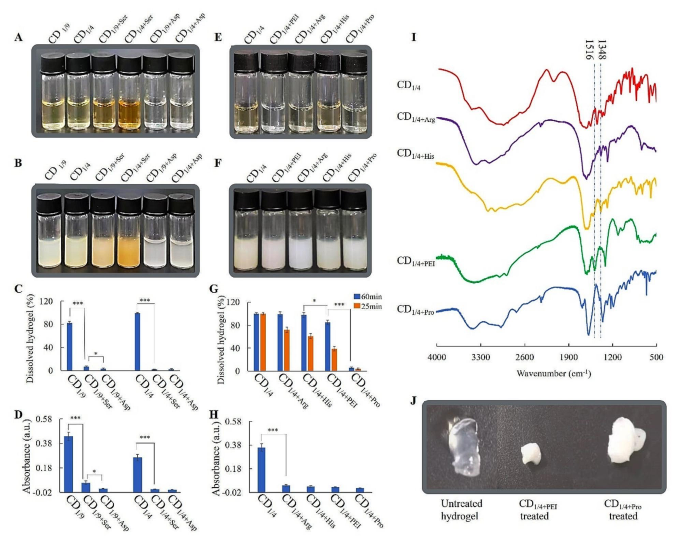
Dissolution of Ca-alginate hydrogels by CDs with totally different N-groups. (A) 18 mg/mL CDSer/CDAsp answer, (B) CDSer/CDAsp added with Ca2+ (remaining focus 3 mM), (C) the ratio of dissolved hydrogels handled with CDSer/CDAsp, (D) absorption of CDSer/CDAsp options from ninhydrin exams, (E) 18 mg/mL CDArg/CDHis/CDProfessional/CDPEI answer, (F) CDArg/CDHis/CDProfessional/CDPEI added with Ca2+ (remaining focus 3 mM), (G) the ratio of dissolved hydrogels handled with CDArg/CDHis/CDProfessional/CDPEI, (H) absorption of CDArg/CDHis/CDProfessional /CDPEI options from ninhydrin exams, (I) FTIR spectra of CDArg/CDHis/CDProfessional/CDPEI, (J) modifications in hydrogel handled with CD1/4+PEI and CD1/4+Professional
To re-verify whether or not major amine teams might keep away from mineralization of alginate, serine (impartial amino acids) and aspartate (acidic amino acid) with comparable molecular weight to lysine (alkaline amino acids) had been chosen because the beginning supplies for preparation of CDs. CDLys, CDAsp and CDSer all produced precipitate with Ca2+, nonetheless, solely CDlys might dissolve Ca-alginate hydrogels (Determine 5A-C). Determine5D confirmed there was little major amine group in CDSer and CDAsp. This take a look at additional verified CDs with giant quantities of major amine teams might keep away from mineralization of alginates and promote gel-sol transition of Ca-alginate hydrogel. In any other case, CDs with little quantities of major amine teams on the floor couldn’t keep away from mineralization of alginates, which blocked the gel-sol transition.
In an effort to examine whether or not different N-groups on floor of CDs might promote dissolution of Ca-alginate hydrogels, PEI, His, Arg and Professional had been chosen because the beginning supplies for preparation of CDs. Determine 5E-G confirmed that every one of those CDs might generate precipitates with Ca2+, nonetheless, the dissolving fee was totally different from one another. Ninhydrin take a look at and FTIR had been used to characterize the N-groups. The ninhydrin reactions of CD1/4+His, CD1/4+Arg, CD1/4+PEI and CD1/4+Professional had been unfavourable, indicating absence of major amine teams (Fig. 5H). As proven in Fig. 5I, the height at 1516 cm− 1 in CDPEI could possibly be assigned to secondary amine teams. The height at 1348 cm− 1 in CDHis and CDArg could possibly be assigned to C-N of secondary amine in histidine/arginine. Determine 5G confirmed hydrogels handled with CDHis or CDArg for 60 min had been utterly dissolved, though the dissolving fee had been slower than that of CDLys. The dissolution could possibly be ascribed to the presence of secondary amine teams in CDHis/CDArg, which kinds H bond with carboxyl in alginates. Determine 5G and J confirmed hydrogel handled with CDProfessional was hardly dissolved and turned from clear to white, indicating mineralization of CDProfessional-treated hydrogel. It additionally could be seen that hydrogel handled with CDPEI was partially dissolved and turned from clear to white finally. The dissolution could possibly be ascribed to the presence of secondary amine teams in CDPEI. After operating out of secondary amine teams, the mineralization occurred on alginate and blocked gel-sol transition. In all, major and secondary amine teams on floor of CDs might promote dissolution of Ca-alginate hydrogels, and CD1/4 baring major amine teams is the best.
In vitro cytotoxicity
As proven in Fig. 6A, oxalic acid exhibited very excessive cytotoxicity even on the focus of 1 mg/mL. Lysine exhibited low cytotoxicity on the focus larger than 18 mg/mL. The cytotoxicity of lysine disappeared after formation of CD0 (Fig. 6B), which could possibly be ascribed to the reducing of solute focus and osmotic stress. When the ratio of oxalic acid to lysine was not more than 1/4, CDs confirmed no cytotoxicity. In any other case, CDs had extraordinarily excessive cytotoxicity. In an effort to examine the rationale of distinction in cytotoxicity, formation of mineralized crystals in cells was noticed at totally different circumstances. Determine S4 confirmed there have been apparent crystals in CD3/4 and CD1 handled cells. The rationale could also be that CD3/4 and CD1 didn’t have sufficient major/secondary amine teams on the floor and subcellular buildings had been additionally concerned within the mineralization of CD3/4/CD1. In any other case, the mineralization occurred solely on CD1/4 with out subcellular buildings. Determine 6C and D revealed CDs had a lot decrease cell viability than bodily mixtures with the identical part at identical ratio. Bodily mixtures even exhibited very excessive cytotoxicity at low focus. The rationale could also be that formation of CDs might cut back the acidity of oxalic acid. In essence, oxalic acid is a robust acid because of the presence of two neighbouring carboxyl teams. One of many carboxyl teams was conjugated to the floor of CDs, which destroyed the construction of neighbouring carboxyl teams. In all, oxalic acid had comparatively excessive cytotoxicity, and its cytotoxicity could possibly be effectively diminished by forming CDs.
Determine S5 revealed cell viabilities had been greater than 95% for each hydrogel extract and sol suspension on the focus of 0.1–10 mg/mL, suggesting good biocompatibility of Ca-alginate hydrogels earlier than and after dissolution
Cytotoxicity and antibacterial impact of CDs. Cytotoxicity of L929 cells handled with (A) beginning supplies of CDs, (B) CDlys on the focus of 18 mg/mL, (C) CD1/4, and bodily combination with the identical ratio of oxalic acid to lysine and (D) CD1/4+Ser, and bodily combination with the identical ratio of oxalic acid to serine; (E) progress curve of E. coli. handled with CD1/4; (F) progress curve of S. aureus. handled with CD1/4; (G) TEM picture of E. coli. handled with 3 mg/mL CD1/4 and (H) TEM picture of E. coli. handled with 18 mg/mL CD1/4
Antimicrobial impact of CD1/4 in opposition to E. coli and S. aureus
CD1/4 on the focus of 18 mg/mL was used to deal with E. coli and S. aureus. Determine 6E and F confirmed the variety of E. coli and S. aureus within the management teams elevated constantly in 6 h. However, CD1/4 remedy led to lower within the first hour and gradual improve inside 2–6 h. These outcomes indicated effectiveness of CD1/4 on the inhibition of E. coli and S. aureus. TEM evaluation was carried out to look at morphological modifications of E. coli. Evenly organized inside constituents was noticed in E. coli handled with 3 mg/mL CD1/4 (Fig. 6G), whereas lack of inside constituents was noticed in E. coli handled with 18 mg/mL CD1/4 (Fig. 6H). In line with earlier stories, oxalic acid can disrupt cell wall integrity by chelating Ca2+ in cell partitions [43]. Thus, it could possibly be inferred that CD1/4 exert antimicrobial impact by destroying cell partitions.
Burn wound therapeutic impact
In vivo wound therapeutic performances. (A) Images of wounds healed at totally different time factors after numerous therapies, (B) share of unhealed wound space, (C) SEM, histological and immunohistochemical staining of wound sections, (D) percentages of collagen deposition space, (E) HIF-1α optimistic cell density, (F) CD68 optimistic cell density
The images and contraction fee of the burn wounds in numerous teams from day 1 to day 24 had been offered in Fig. 7A and B. Ranging from day 12, the injuries handled with dissolving hydrogels had been healed considerably sooner than management and/or hydrogel teams. The burn wound was virtually utterly recovered on day 24 within the hydrogel + CD1/4 group, whereas seen wounds had been nonetheless observable in different teams. H&E and Masson trichrome staining had been used to evaluate the histopathological buildings of wound tissue from regenerated pores and skin on day 16. As proven in Fig. 7C, there was nonetheless epidermal rupture in management group. From Masson’s trichrome-stained pictures, it was noticed that wound handled with dissolvable hydrogel produced tremendously extra collagen than different teams (Fig. 7D). Above outcomes revealed that the Ca-alginate hydrogel with substitute enhanced re-epithelialization and collagen manufacturing. SEM pictures confirmed the newly shaped hydrogels on wounds had porous buildings, whereas the opposite two teams had been practically nonporous on day 17. The porous construction in hydrogel permits air circulation, oxygen provide and wound exudate absorption throughout wound therapeutic course of [44]. However the exudate wound block the holes of hydrogels [19]. To evaluate whether or not Ca-alginate hydrogel with substitute might alleviate hypoxia, new generated tissues had been noticed by HIF-1α immunostaining (brown cells). The relative HIF-1α expression within the hydrogel + CD1/4 group was considerably decrease than that in management and hydrogel solely teams (Fig. 7E), proving hypoxia aid of replaceable hydrogels. Native irritation additionally exerts a key impact on wound therapeutic. The hydrogel with substitute confirmed a lot decrease CD68-positive macrophage (brown cells) density than the opposite two teams (Fig. 7F). These outcomes indicated that dissolvable hydrogel might successfully alleviate native inflammatory reactions. This could possibly be ascribed to the improved oxygen provide of hydrogels and antibacterial properties of CDs. In line with earlier stories, improved oxygen provide might speed up the decision of the preliminary irritation part and the development of the proliferation part [45].