April 17, 2024
On the similar time, fraudsters remained extremely lively. They used all types of malicious apps to execute totally different fraudulent schemes.
Google Play as soon as once more was the item of cybercriminals’ curiosity. Throughout final 12 months, Physician Net’s virus laboratory found over 400 trojan packages on it, with cumulative downloads of a minimum of 428 million.
As well as, our specialists found extra trojan packages designed to steal crypto forex, and attackers have been as soon as once more concentrating on not solely Android system customers but in addition these with iOS gadgets.
PRINCIPAL TRENDS IN 2023
- A rise in ad-displaying trojan exercise
- A lower in banking trojan exercise
- The emergence of latest Android banking malware concentrating on Russian and Iranian customers
- The emergence of many new threats on Google Play
- Fraudsters remaining extremely lively
- The emergence of latest trojan apps designed to steal crypto forex from customers of Android and iOS-based gadgets
Essentially the most notable occasions of 2023
In Might, on Google Play, Physician Net uncovered over 100 apps containing the built-in SpinOk module. This module positioned itself as a specialised advertising and marketing platform that may be embedded into Android video games and packages. This instrument was designed to take care of customers’ curiosity in apps with the assistance of mini video games, a system of duties, and alleged prizes and reward drawings. Nonetheless, it had spyware and adware performance and was, due to this fact, added to the Dr.Net virus database as Android.Spy.SpinOk. The module collected data on information saved on gadgets and was capable of switch them to malicious actors. It may additionally substitute and add clipboard contents to a distant server in addition to show promoting banners, resembling these proven within the examples beneath:
In complete, the apps found to include Android.Spy.SpinOk have been downloaded greater than 421 million instances. After contacting our firm, SpinOk’s developer made corrections to the module. Because of this, the two.4.2 platform model, present on the time of the repair, not had the trojan performance.
In early September, Physician Net printed a examine of the Android.Pandora.2 backdoor, which was primarily concentrating on Spanish-speaking customers. A lot of assaults involving this malware have been recorded in March 2023. The primary modifications of this trojan had been added to the Dr.Net anti-virus database in June 2017. Android.Pandora.2 and its varied modifications infect Android-based Good TV units and TV containers through compromised firmware updates and when customers set up trojan variations of purposes used to view pirated video content material on-line. Under are examples of internet sites that unfold this backdoor:
The trojan creates a botnet of contaminated gadgets and upon receiving the attackers’ instructions can execute DDoS assaults of varied varieties. It will possibly additionally carry out quite a lot of different malicious actions, like putting in its personal updates and substituting the unique system hosts file. The evaluation our specialists carried out confirmed that when creating this backdoor, its authors borrowed from the authors of Linux.Mirai, taking a part of its code and utilizing it as the premise for his or her trojan. In flip, since 2016, Linux.Mirai has been extensively used to contaminate IoT (the “Web of issues”) gadgets and to carry out DDoS assaults on varied web sites.
That very same month, Physician Net’s malware analysts reported instances the place the Android.Spy.Lydia multi-functional spyware and adware trojan was being distributed; these malicious packages have been concentrating on Iranian customers. Members of this household are disguised as a web-based buying and selling platform, and menace actors can command them to carry out quite a lot of malicious actions. For instance, they will intercept and ship SMS, acquire information about phonebook contacts, hijack clipboard contents, load phishing web sites, and so on. Android.Spy.Lydia trojans can be utilized in several fraudulent schemes and to steal private information. Furthermore, with their assist, malicious actors can steal victims’ cash.
On the finish of September, our firm warned customers concerning the improve in instances of fraud utilizing distant administration software program for cellular gadgets. This allowed menace actors to realize full management over customers’ Android gadgets. Posing as credit score organizations’ assist workers, cybercriminals knowledgeable potential victims about “suspicious exercise” occurring with their financial institution accounts and requested them to obtain a “financial institution assist app”. In actuality, this system in query was a distant desktop entry instrument, and most frequently it was the RustDesk Distant Desktop app. After this instrument was blocked on Google Play, menace actors started distributing it through fraudulent web sites. And in some instances, they modified this system to be extra convincing. For this, they changed the icon and the title with these equivalent to a specific financial institution. Dr.Net anti-virus detects trojan variations of this program as Android.FakeApp.1426.
On the similar time, in 2023, Physician Net’s specialists continued to determine malicious web sites by way of which cybercriminals have been distributing faux crypto-wallet software program for Android and iOS gadgets to be able to steal crypto currencies.
Statistics
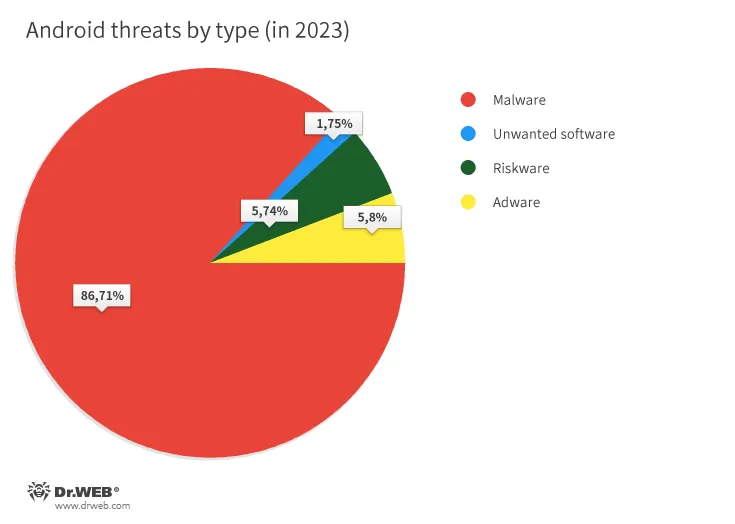
In 2023, with a share of 86.71% of all Dr.Net anti-virus detections, malicious packages have been as soon as once more the commonest Android threats. Adware, with a share of 5.80%, got here in second. The third commonest Android threats have been probably harmful packages, or riskware; these have been detected on protected gadgets in 5.74% of instances. And in 1.75% of instances, customers encountered undesirable software program.
Risk distribution by sort, based mostly on the Dr.Net anti-virus detection statistics for cellular gadgets, is proven within the following diagram:
Malicious packages
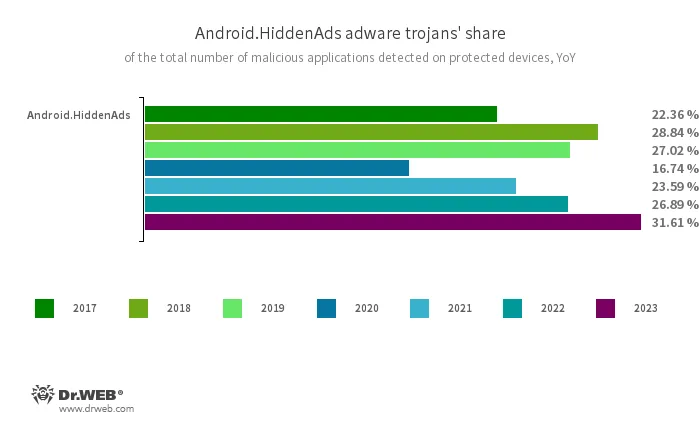
Trojans from the Android.HiddenAds household have been the commonest malicious Android apps. Their share within the complete variety of malware detected by Dr.Net anti-virus elevated by 4.72 pp, in comparison with 2022, and was 31.61%.
Android.HiddenAds.3697 was essentially the most lively member of the household; it was detected on protected gadgets in 10.72% of instances. Totally different variants of this trojan horse have remained leaders by way of variety of detections. For instance, the Android.HiddenAds.1994 modification was essentially the most widespread in 2021, whereas the Android.HiddenAds.3018 turned the chief in 2022. In 2023, together with Android.HiddenAds.3697, our specialists additionally discovered some extra modifications of this trojan, together with Android.HiddenAds.3597, Android.HiddenAds.3831, Android.HiddenAds.3851, and Android.HiddenAds.3956. It’s doable that over time certainly one of them may even be capable of take the main place.
The second commonest have been Android.Spy trojans, which possess spyware and adware performance. In comparison with 2022, their share within the complete quantity of malware detected by Dr.Net anti-virus decreased by 14.01 pp. and amounted to twenty-eight.22%. Essentially the most lively amongst them was Android.Spy.5106. It accounted for 20.80% of all malware detections. And, if we bear in mind the sooner variants of this trojan—Android.Spy.4498 and Android.Spy.4837, its share was 24.32%, or virtually 1 / 4 of all detections.
Advert-displaying trojans from the Android.MobiDash household got here in third. Their share within the complete quantity of malware detections elevated by 5.25 pp. and went as much as 10.06%.
Malicious packages designed to load and set up different apps and able to working arbitrary code continued to be much less lively in 2023. As an illustration, the share of Android.DownLoader trojan household detections decreased by 1.58 pp. to 2.18%, Android.Triada ― by 0.99 pp. to 2.14%, and Android.RemoteCode ― by 0.01 pp. to 2.83%. The share of Android.Mobifun detections decreased by 0.33 pp. to 0.25% and Android.Xiny by 0.21 pp. to 0.27%.
On the similar time, the variety of assaults utilizing Android.FakeApp malicious faux packages elevated. Cybercriminals used these in varied fraudulent schemes. Final 12 months, their share within the complete variety of malware detected by the Dr.Net anti-virus was 1.83%, which is 0.85 pp. larger than the 12 months earlier than.
In 2023, the exercise of Android.Locker ransomware trojans decreased. Their share within the complete variety of malware purposes detected got here all the way down to 1.15%, from 1.50% the 12 months earlier than. On the similar time, the variety of Android.Packed detections elevated. These are malicious packages of varied varieties which might be protected with software program packers. The variety of their detections elevated by 5.22 pp. to 7.98%.
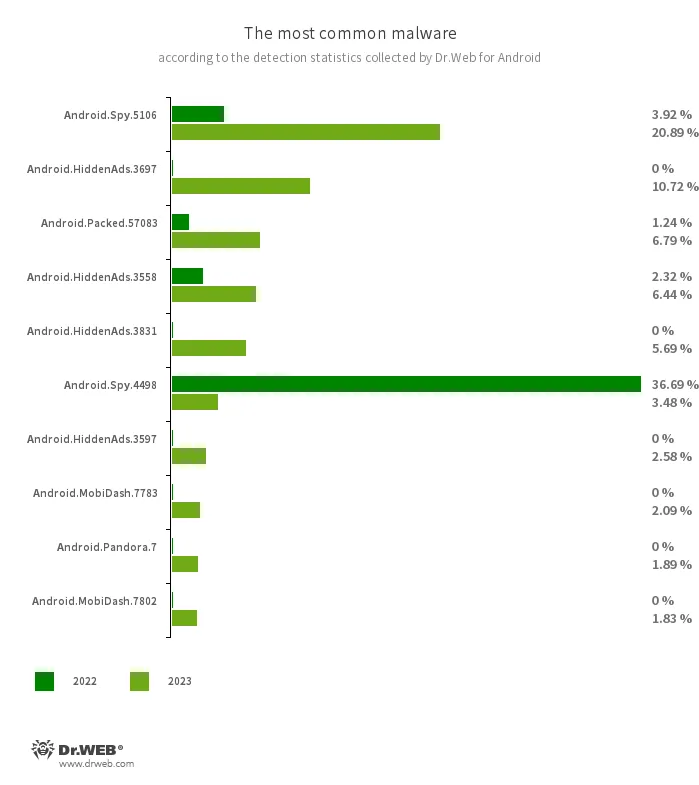
The ten mostly detected malicious purposes in 2023 are proven within the following graph:
- Android.Spy.5106
- Android.Spy.4498
- The detection title for various variants of the trojan that presents itself as modified variations of unofficial WhatsApp messenger mods. This trojan horse can steal the contents of notifications and supply customers different apps from unknown sources for set up. And when such a modified messenger is used, it might probably additionally show dialog containers containing remotely configurable content material.
- Android.HiddenAds.3697
- Android.HiddenAds.3558
- Android.HiddenAds.3831
- Android.HiddenAds.3597
- Trojan apps designed to show intrusive adverts. Trojans of this household are sometimes distributed as widespread and innocent purposes. In some instances, different malware can set up them within the system listing. When these infect Android gadgets, they sometimes conceal their presence from the consumer. For instance, they “conceal” their icons from the house display screen menu.
- Android.Packed.57083
- The detection title for malicious purposes protected with an ApkProtector software program packer. Amongst them are banking trojans, spyware and adware, and different malicious software program.
- Android.MobiDash.7783
- Android.MobiDash.7802
- These are trojans that show obnoxious adverts. They arrive as a particular software program module that builders incorporate into purposes.
- Android.Pandora.7
- The detection title for malicious packages that obtain and set up the Android.Pandora.2 backdoor trojan. Risk actors typically embed such downloaders in Good TV software program oriented towards Spanish-speaking customers.
Undesirable software program
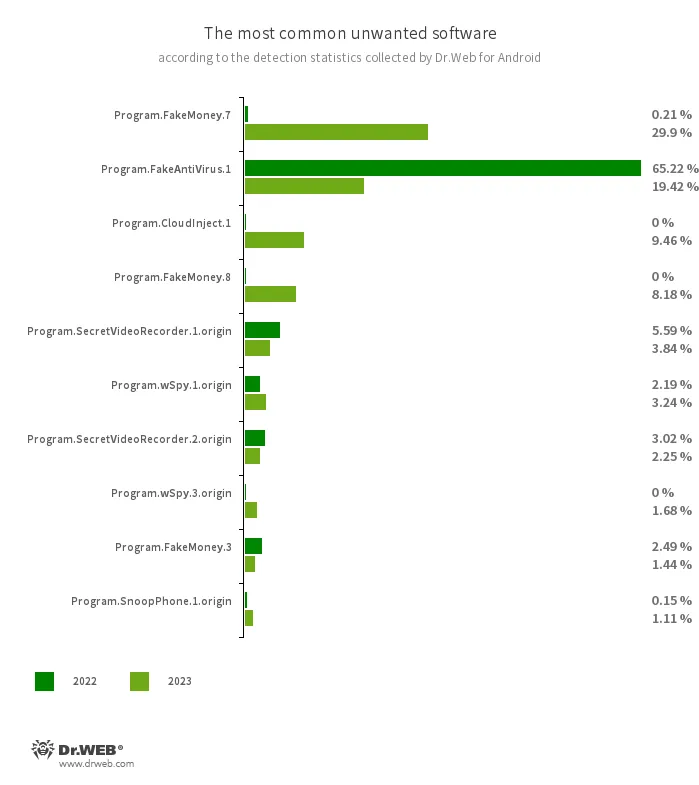
The commonest undesirable program in 2023 was Program.FakeMoney.7; it accounted for 29.90% or virtually one third of the entire variety of detections of threats of this sort. It belongs to a household of packages that supply customers the chance to earn a living by finishing varied duties however don’t really pay out any actual rewards.
The chief of 2022, Program.FakeAntiVirus.1, dropped to second place a 12 months later with a share of 19.42% detections. This program simulates anti-virus conduct, detects nonexistent threats and affords Android system homeowners the chance to purchase its full model to “repair” supposedly recognized issues.
Third place, with a share of 9.46%, is held by packages which might be modified through the CloudInject cloud service; Dr.Net anti-virus detects such purposes as Program.CloudInject.1. In the course of the modification course of, harmful permissions and obfuscated code are added to them. There isn’t any approach of controlling the code’s objective.
As within the 12 months earlier than, in 2023 customers typically encountered packages that enable their actions to be monitored and varied data to be collected about them. Risk actors can use such apps to spy illegally on Android system homeowners. Amongst these packages, essentially the most generally detected ones have been Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin (3.84% of instances), Program.wSpy.1.origin (3.24% of instances), Program.SecretVideoRecorder.2.origin (2.25% of instances), Program.wSpy.3.origin (1.68% of instances), Program.SnoopPhone.1.origin (1.11% of instances), Program.Reptilicus.8.origin (0,98% of instances) and Program.WapSniff.1.origin (0,83% of instances).
The ten mostly detected undesirable packages in 2023 are listed within the following graph:
- Program.FakeMoney.7
- Program.FakeMoney.8
- Program.FakeMoney.3
- The detection title for Android purposes that allegedly enable customers to earn cash by watching video clips and adverts. These apps make it look as if rewards are accruing for accomplished duties. To withdraw their “earnings”, customers allegedly have to gather a sure sum. However even when they succeed, in actuality they can not get any actual funds.
- Program.FakeAntiVirus.1
- The detection title for adware packages that imitate anti-virus software program. These apps inform customers of nonexistent threats, mislead them, and demand that they buy the software program’s full model.
- Program.CloudInject.1
- The detection title for Android packages which were modified utilizing the CloudInject cloud service and the eponymous Android utility (the latter was added to the Dr.Net virus database as Device.CloudInject). Such packages are modified on a distant server; in the meantime, the modders (customers) who’re curious about such modifications can’t management precisely what might be added to the apps. Furthermore, these packages obtain quite a lot of harmful system permissions. As soon as modification is full, customers can remotely handle these apps. They will block them, show customized dialogs, and monitor when different software program is being put in or faraway from a tool, and so on.
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.1.origin
- Program.SecretVideoRecorder.2.origin
- The detection title for varied modifications of an utility that’s designed to document movies and take images within the background utilizing built-in Android system cameras. It will possibly function covertly by permitting notifications about ongoing recordings to be disabled. It additionally permits an app’s icon and title to get replaced with faux ones. This performance makes this software program probably harmful.
- Program.wSpy.1.origin
- Program.wSpy.3.origin
- These are variants of a business spyware and adware app designed to covertly monitor Android system consumer exercise. This program permits intruders to learn SMS and chats in widespread messaging software program, hearken to the environment, monitor system location and browser historical past, achieve entry to the phonebook and contacts, images and movies, and take screenshots and footage by way of a tool’s built-in digital camera. As well as, it has keylogger performance.
- Program.SnoopPhone.1.origin
- An utility designed to observe the exercise of Android system homeowners. It permits intruders to learn SMS, acquire name data, monitor system location, and document the environment.
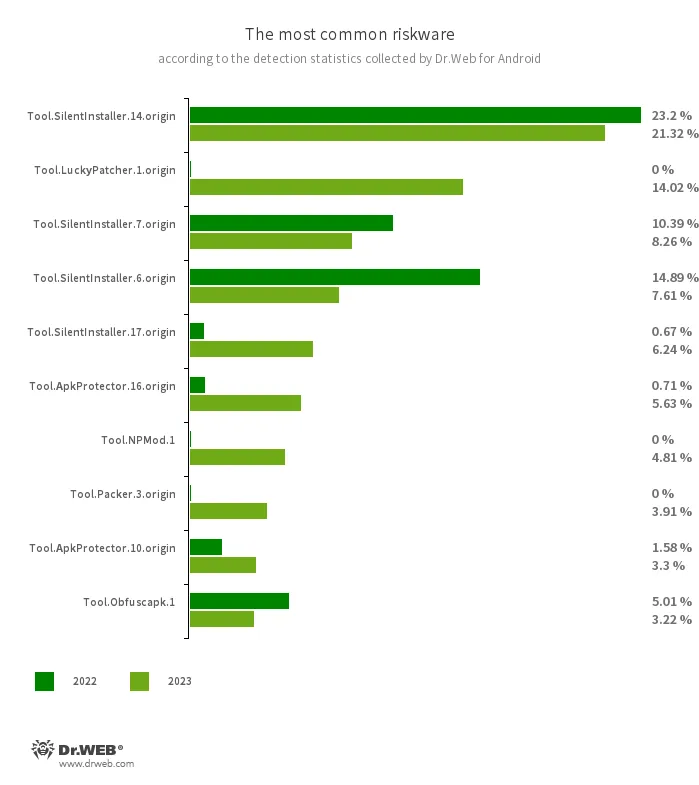
Riskware
Essentially the most generally detected riskware packages in 2023 have been as soon as once more the Device.SilentInstaller utilities, which permit Android apps to run with out being put in. They don’t seem to be malicious, however menace actors can use them for launching malware. These instruments accounted for 48.98% or virtually half of the possibly harmful software program detections. On the similar time, in comparison with 2022, their share decreased by 17.94 pp. The second most widespread probably harmful packages have been members of the Device.LuckyPatcher household of utilities. These can be utilized to switch Android purposes and add particular scripts downloaded from the Web to them. These instruments accounted for 14.02% of riskware detections. In third place have been apps protected with Device.ApkProtector packer; the variety of their detections elevated by 5.33 pp. and reached 10.14%.
On the similar time, the variety of detections of apps protected with different households of software program packers additionally elevated. As an illustration, the Device.Packer household’s share elevated from 3.58% to 4.47%, and the Device.Ultima household’s share elevated from 0.05% to 1.04%.
One other widespread, probably harmful software program program was the NP Supervisor utility. It’s designed to switch Android packages and bypass their digital signature verification. To perform this, a particular module is embedded into them. Dr.Net anti-virus detects such modified apps as Device.NPMod. The share of such apps was 4.81%.
In distinction, apps modified with the Device.Obfuscapk obfuscator instrument have been detected much less typically, and their share decreased from 5.01% in 2022 to three.22% in 2023.
The ten most widespread riskware apps detected on protected Android gadgets in 2023 are proven within the following graph:
- Device.SilentInstaller.14.origin
- Device.SilentInstaller.7.origin
- Device.SilentInstaller.6.origin
- Device.SilentInstaller.17.origin
- Riskware platforms that enable purposes to launch APK information with out putting in them. They create a digital runtime surroundings within the context of the apps wherein they’re built-in. The APK information, launched with the assistance of those platforms, can function as if they’re a part of such packages and may also receive the identical permissions.
- Device.LuckyPatcher.1.origin
- A instrument that enables apps put in on Android gadgets to be modified (i.e., by creating patches for them) to be able to change the logic of their work or to bypass sure restrictions. As an illustration, customers can apply it to disable root-access verification in banking software program or to acquire limitless assets in video games. So as to add patches, this utility downloads specifically ready scripts from the Web, which will be crafted and added to the frequent database by any third occasion. The performance of such scripts can show to be malicious; thus, patches made with this instrument can pose a possible menace.
- Device.ApkProtector.16.origin
- Device.ApkProtector.10.origin
- The detection title for Android apps protected by the ApkProtector software program packer. This packer shouldn’t be malicious in itself, however cybercriminals can use it when creating malware and undesirable purposes to make it tougher for anti-virus software program to detect them.
- Device.NPMod.1
- The detection title for Android packages which were modified utilizing the NP Supervisor utility. A particular module is embedded in such apps, and it permits them to bypass digital signature verification as soon as they’ve been modified.
- Device.Packer.3.origin
- The detection title for Android packages whose code is encoded and obfuscated by the NP Supervisor instrument.
- Device.Obfuscapk.1
- The detection title for purposes protected by the Obfuscapk obfuscation instrument. This instrument is used to routinely modify and scramble Android app supply code to make reverse engineering tougher. Cybercriminals use it to guard malicious purposes from being detected by anti-virus packages.
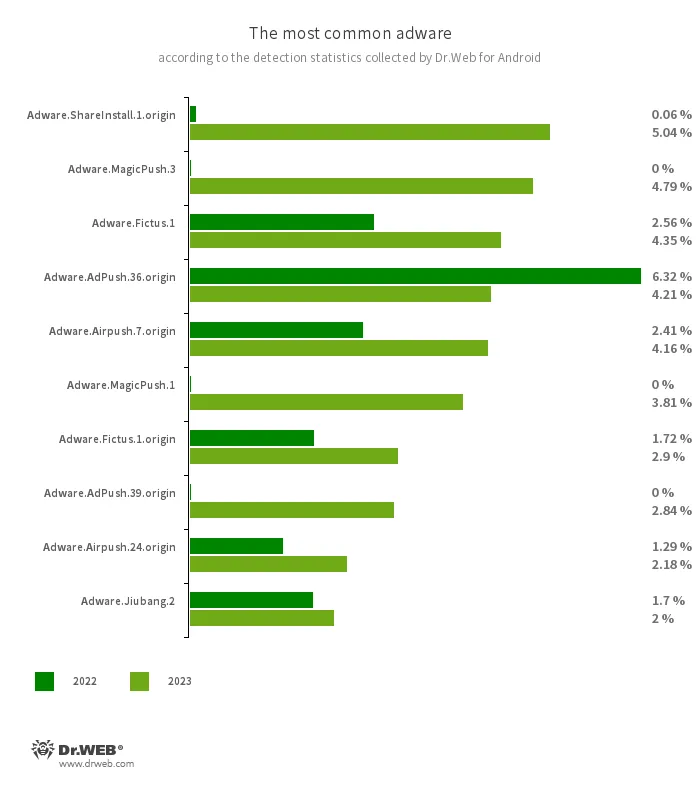
Adware
The most well-liked adware in 2023 was Adware.Adpush, a household of promoting modules constructed into some Android apps. They accounted for greater than a 3rd of detections — 35.82%; in comparison with 2022, their share decreased by 24.88 pp. The second commonest adware packages have been members of the Adware.MagicPush household with a share of 9.58%. Third place was held by Adware.Airpush modules whose share elevated by 3.24 pp., they usually accounted for 8.59% of detections.
Additionally among the many leaders have been representatives of the Adware.ShareInstall household, whose share elevated from 0.06% to five.04%, Adware.Fictus (with progress from 2.58% to 4.41%), Adware.Leadbolt (with progress from 3.31% to 4.37%), Adware.Jiubang (with progress from 2.83% to three.22%), and Adware.Youmi (with progress from 0.06% to 2.20%).
On the similar time, Adware.SspSdk modules, which occupied second place the 12 months earlier than, didn’t even make it into the highest 10 most widespread households in 2023. They accounted for 1.49% of the adware detected on protected gadgets.
The ten mostly detected adware apps detected on protected gadgets in 2023 are proven within the graph beneath:
- Adware.ShareInstall.1.origin
- An adware module that may be constructed into Android purposes. It shows notifications containing adverts on the Android OS lock display screen.
- Adware.MagicPush.1
- Adware.MagicPush.3
- An adware module embedded into Android purposes. It shows pop-up banners over the OS consumer interface when such internet hosting apps are usually not in use. These banners include deceptive data. Most frequently, they inform customers about suspicious information which have allegedly been found, or they provide to dam spam for customers or to optimize their system’s energy consumption. To do that, they ask customers to open the corresponding app containing such an adware module. Upon opening the app, customers are proven an advert.
- Adware.Fictus.1
- Adware.Fictus.1.origin
- An adware module that malicious actors embed into the cloned variations of widespread Android video games and purposes. Its incorporation is facilitated by a specialised net2share packer. Copies of software program created this manner are then distributed by way of varied software program catalogs. When put in on Android gadgets, such apps and video games show obnoxious adverts.
- Adware.AdPush.36.origin
- Adware.AdPush.39.origin
- Adware modules that may be constructed into Android apps. They show notifications containing adverts that mislead customers. For instance, such notifications can appear like messages from the working system. As well as, these modules acquire quite a lot of confidential information and are capable of obtain different apps and provoke their set up.
- Adware.Airpush.7.origin
- Adware.Airpush.24.origin
- A household of adware modules that may be constructed into Android apps and show varied adverts. Relying on the modules’ model and modification, these will be notifications containing adverts, pop-up home windows or banners. Malicious actors typically use these modules to distribute malware by providing their potential victims numerous software program for set up. Furthermore, such modules acquire private data and ship it to a distant server.
- Adware.Jiubang.2
- An adware module constructed into Android packages. It attracts commercial banners over different app home windows.
Threats on Google Play
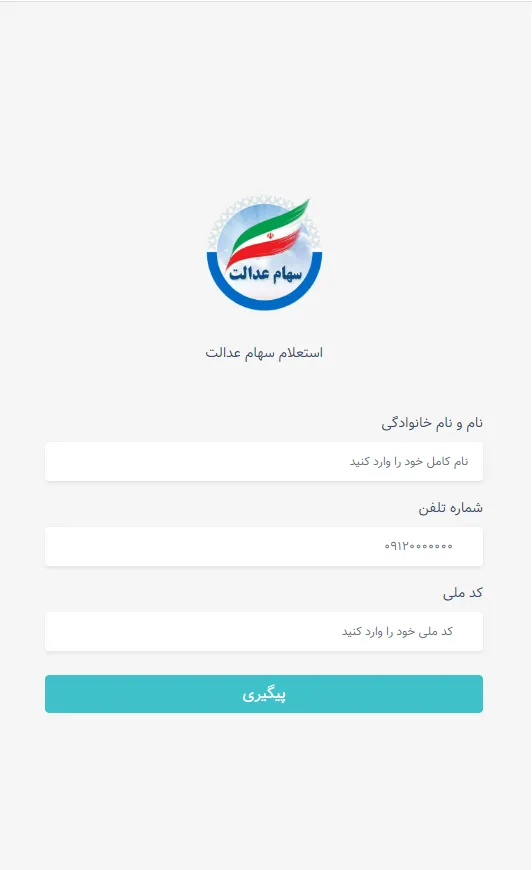
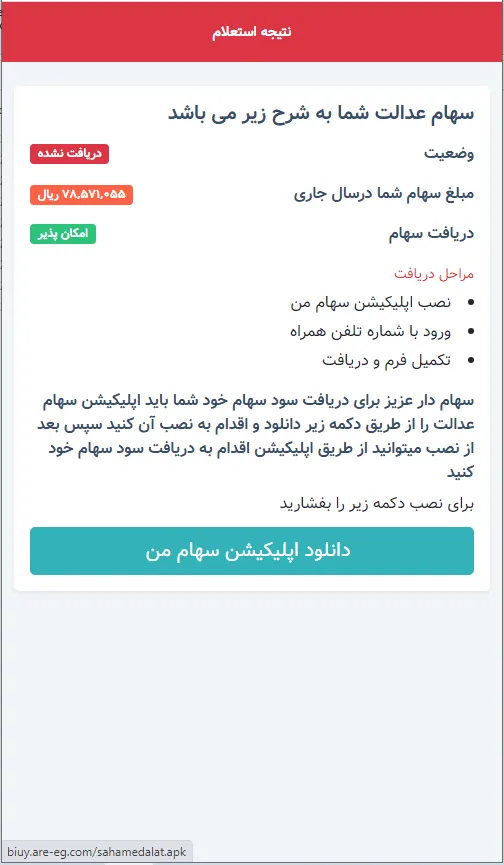
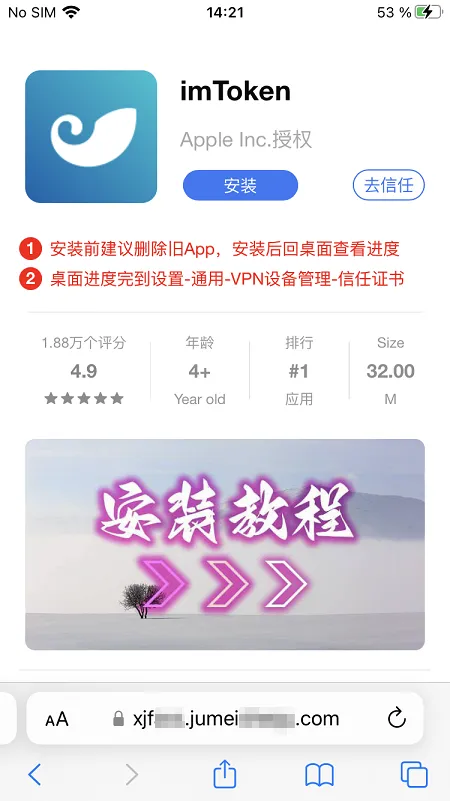
In 2023, Physician Net’s virus laboratory found over 440 malicious packages on Google Play, with an total obtain depend of a minimum of 428,434,576. Among the many many packages containing the built-in Android.Spy.SpinOk trojan module (lined in one of many earlier paragraphs), our specialists discovered a whole lot of trojans from the Android.FakeApp household. Utilized by cybercriminals to execute totally different fraudulent schemes, these trojans have been distributed underneath the guise of quite a lot of software program. Underneath sure circumstances, they really may present the promised performance, however their major process was to load goal web sites when commanded to take action by a distant server.
Many of those trojans have been handed off as finance-themed apps, like instructing aids and reference books, packages for residence bookkeeping or accessing inventory data and buying and selling, apps for collaborating in surveys, and so on.
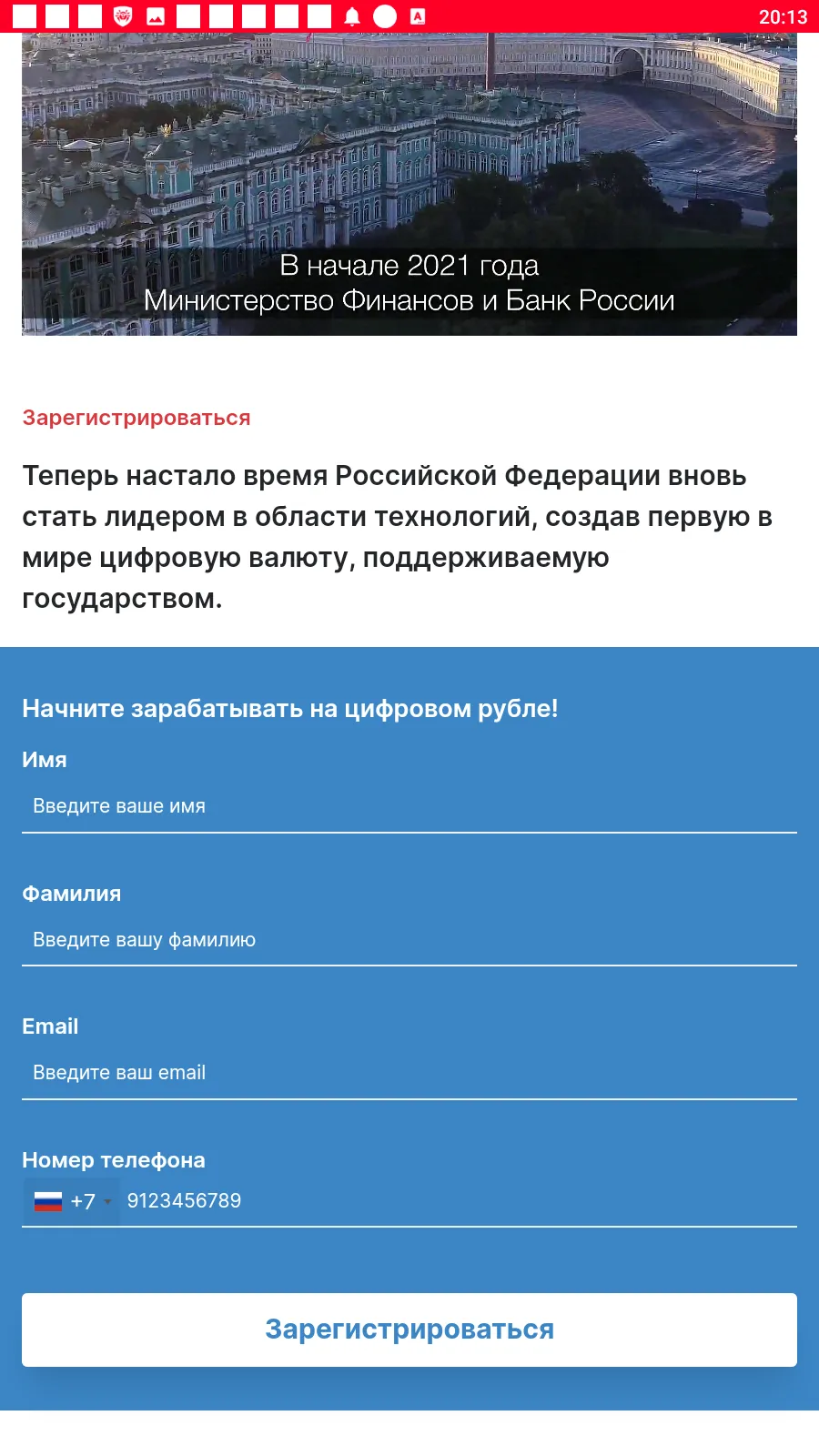
Such faux packages may load fraudulent websites the place potential victims have been provided, allegedly on behalf of well-known firms, a chance to earn a living through investments and crypto-currency buying and selling, and, in some instances, to even obtain firm shares or authorities funds — each “as a present”. To “entry” one or one other service, customers first needed to reply a number of questions after which present some private information.
Under are examples of the fraudulent web sites these trojans loaded. Within the first case, scammers provided customers the chance to entry some investing platform, one supposedly associated to a big Russian oil and fuel firm. Within the second case, fraudsters, allegedly on behalf of The Central Financial institution of the Russian Federation, provided potential victims the possibility to start out “being profitable with the Digital ruble”.
A few of these faux apps have been distributed underneath the guise of video games; they might load on-line on line casino and bookmaker web sites.
Examples of how such trojan apps operated as video games:
Examples of the bookmaker and on-line on line casino web sites they loaded:
Different Android.FakeApp trojans have been distributed as sports-themed packages, together with supposedly official software program from authorized bookmaker corporations, reference books on varied sports activities, apps that offered details about sporting occasions and matches, packages for studying sports activities information, and so forth.
They may additionally work as innocent apps (their performance may, nevertheless, differ from what was promised) and cargo totally different web sites.
Under are examples of how these trojans operated as innocent software program: two of them launched as video games, whereas the third one displayed a desk containing details about soccer matches.
The identical packages later started loading websites providing bookmaker companies:
Customers put in some faux packages, considering that they have been job-search apps.
Such Android.FakeApp trojan variants show faux emptiness listings which might be loaded from bogus web sites. When customers attempt to answer one of many “job affords”, they’re requested both to contact the “employer” through messengers like WhatsApp and Telegram or to enter their private information right into a particular kind—allegedly for creating and sending out a resume.
On the similar time, in 2023, the subject of Android.FakeApp faux packages, which loaded fraudulent Web assets, continued to broaden. For instance, towards the backdrop of a few years of cybercriminals making an attempt to lure customers to faux monetary websites, our specialists famous the emergence of trojan variants that have been masquerading as authorized packages, like reference books. These supposedly may assist victims of “investing” scammers get again misplaced cash. In actuality, these apps would load extra fraudulent websites that operated in line with a well known scheme. On this case, their guests needed to reply a number of questions after which present some private information to be able to “get a free session with a lawyer”.
An instance of a “authorized help” web site the place victims of funding scams may allegedly seek the advice of with a lawyer and get an opportunity to get their misplaced a reimbursement:
Physician Net’s virus laboratory additionally uncovered quite a lot of different malicious packages on Google Play in 2023. Amongst them have been trojans from the brand new Android.Proxy.4gproxy household that turned contaminated gadgets into proxy servers and covertly transmitted third-party site visitors by way of them. A particular utility known as 4gproxy (added to the Dr.Net virus database because the riskware software program Device.4gproxy) was constructed into these malicious apps. This utility permits Android gadgets for use as proxy servers. It isn’t malicious in itself and can be utilized for respectable functions. Nonetheless, within the case of Android.Proxy.4gproxy trojans, the proxy server operation was executed with out customers’ involvement and their express consent.
Furthermore, our specialists found a number of new ad-displaying trojans from the Android.HiddenAds household: Android.HiddenAds.3785, Android.HiddenAds.3781, Android.HiddenAds.3786, and Android.HiddenAds.3787. When put in on Android gadgets, they tried to hide their presence by changing their icons on the house display screen menu with clear variations and altering their names in order that they have been left clean. Moreover, they might additionally disguise themselves as a Google Chrome internet browser by changing their icons with the corresponding copy. When customers clicked on certainly one of these modified icons, the trojans would mislead them by launching the browser and concurrently persevering with to work within the background. Consequently, not solely did they make themselves much less noticeable, however in addition they elevated their possibilities of working longer. If, for some cause, the trojans would cease working, customers may restart them, mistakenly considering that they have been launching the browser. Such performance was beforehand seen, for instance, within the Android.HiddenAds.3766 trojan, which was additionally distributed through Google Play.
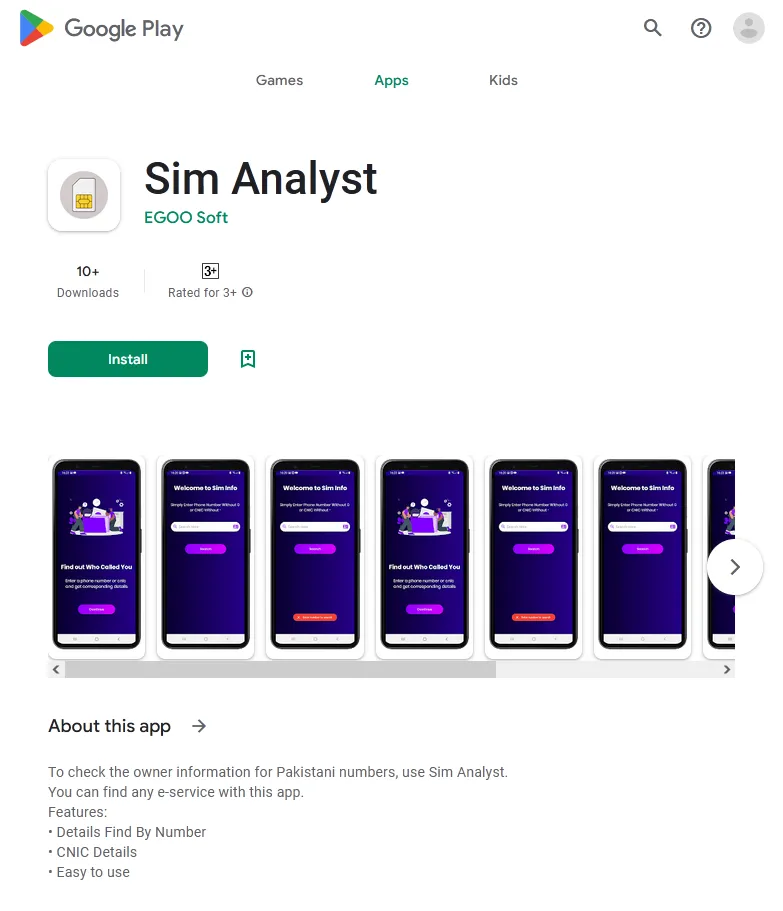
The Android.Spy.1092.origin spyware and adware trojan, which was based mostly on a distant administration instrument (or RAT) known as AhMyth Android Rat, was one other menace our analysts found. It was disguised because the Sim Analyst app, which allegedly may assist Pakistani customers search details about fellow Pakistani mobile community subscribers by getting into their cell phone numbers.
The usual model of the AhMyth Android Rat spyware and adware instrument supplies wealthy performance. As an illustration, it permits an Android system’s location to be tracked, images to be taken through the built-in digital camera and recordings to be fabricated from the environment through the microphone. Moreover, it might probably intercept SMS and acquire data on telephone calls and phonebook contacts. Nonetheless, since apps distributed through Google Play have restricted entry to sure delicate features, the spyware and adware variant our malware analysts found was not so feature-rich. It may monitor a tool’s location, hijack the contents of notifications, and steal varied media information, resembling images and movies, and likewise information that have been transferred through messengers and saved regionally on a tool.
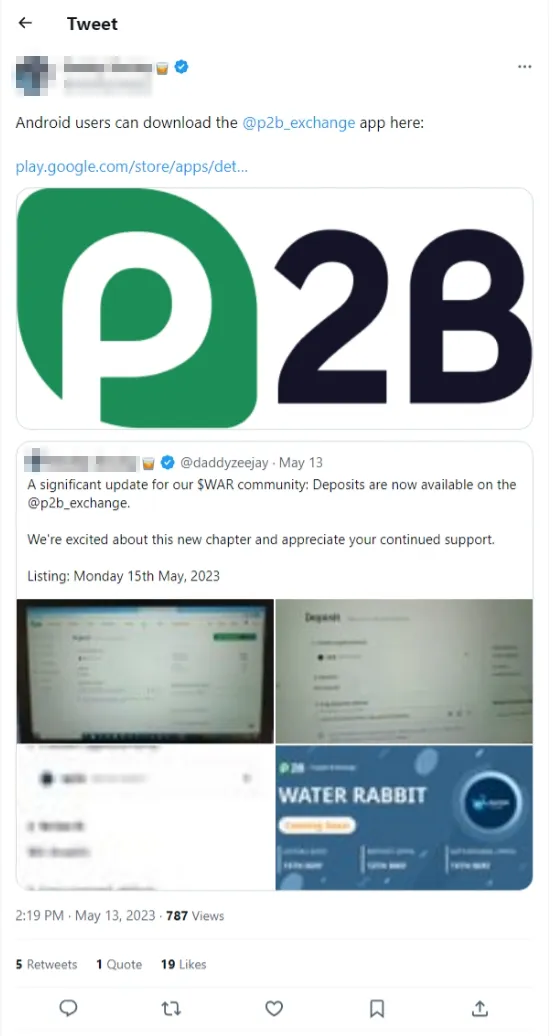
Our specialists additionally detected the Android.CoinSteal.105 trojan on Google Play. It was designed to steal crypto forex. Attackers tried passing it off because the official utility of the P2B crypto trade (P2B official) by utilizing an analogous title: “P2B Commerce: Notice The P2Pb2b”.
The primary picture beneath depicts the faux app’s web page on Google Play, whereas the second picture depicts the web page of the real software program:
On the similar time, the phony utility was even promoted by crypto bloggers. Because of this, it was put in twice as many instances as the unique.
When launched, Android.CoinSteal.105 would load in WebView the TDS (Site visitors Supply System) web site specified by the attackers. This web site would then carry out a series of redirects to different Web assets. For instance, it could load the official web site of the P2P crypto trade: https://p2pb2b.com. The trojan would inject JavaScript scripts into it. Utilizing these scripts, it could substitute the crypto-wallet addresses that customers entered to withdraw crypto forex. That being mentioned, different websites may probably have been loaded as properly, together with fraudulent ones or ones containing adverts.
Among the many threats on Google Play recognized by Physician Net’s virus laboratory have been additionally some new trojans from the Android.Subscription household—Android.Subscription.19, Android.Subscription.20, and Android.Subscription.21. They have been distributed underneath the guise of innocent apps and loaded web sites of affiliate companies to subscribe Android system homeowners to paid companies. Such trojans both activate subscriptions routinely or ask potential victims to supply their cell phone quantity.
Examples of internet sites that these malicious apps load to activate paid subscriptions:
On the similar time, over the course of 2023, different malicious packages that subscribed customers to paid companies have been additionally found on Google Play. Of specific notice are over 20 trojans from the Android.Joker and Android.Harly households. Amongst them have been Android.Joker.1991, Android.Joker.2000, Android.Joker.2117, Android.Joker.2152, Android.Joker.2176, Android.Joker.2217, Android.Harly.13, Android.Harly.25, Android.Harly.66, and Android.Harly.80.
Banking trojans
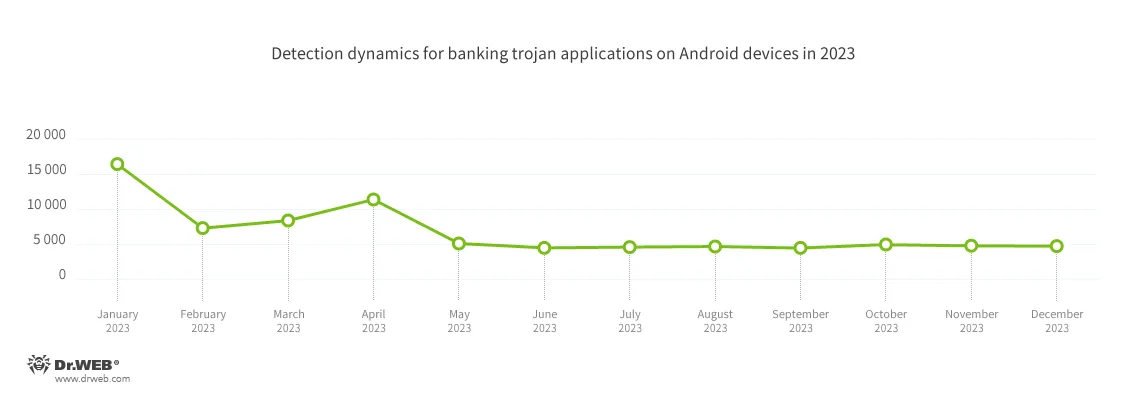
In accordance with detection statistics collected by Dr.Net for Android, the variety of banking trojans detected in 2023 decreased by 46.97%, in comparison with the earlier 12 months. With that being mentioned, their share of all of the malware detected on protected gadgets amounted to three.58%, which is 0.84 pp. lower than the 12 months earlier than. The very best banking trojan exercise occurred within the first half of the 12 months, with the utmost variety of detections occurring in January. After a steep decline in February, their exercise started rising once more and reached a neighborhood peak in April. Following one other decline within the variety of assaults in Might, the variety of banking trojans detected remained fixed till the tip of the 12 months.
The banking trojans hottest with cybercriminals in 2022 additionally remained lively throughout 2023. As an illustration, our analysts detected assaults involving households like Anubis (Android.BankBot.670.origin, Android.BankBot.794.origin, Android.BankBot.967.origin), Coper, S.O.V.A. (Android.BankBot.992.origin), Hydra (Android.BankBot.1048.origin), Ermac (Android.BankBot.970.origin, Android.BankBot.1037.origin), and Alien (Android.BankBot.745.origin, Android.BankBot.873.origin, Android.BankBot.1078.origin). Risk actors additionally distributed malicious packages like Cerberus (Android.BankBot.8705, Android.BankBot.1052.origin), Sharkbot (Android.BankBot.977.origin), and GodFather (Android.BankBot.1064.origin, Android.BankBot.1077.origin).
In Latin America, Banbra (Android.BankBot.1073.origin) banking trojans have been widespread once more, and customers from Brazil additionally encountered the PixPirate (Android.BankBot.1026.origin) household.
The widespread MoqHao household (Android.Banker.5063, Android.Banker.487.origin, Android.Banker.533.origin, Android.Banker.657.origin), whose assaults embody many international locations, was actively used towards Southeast Asian and Asia-Pacific Android customers. In the meantime, South Korean customers additionally encountered totally different members of the Fakecalls (Android.BankBot.761.origin, Android.BankBot.919.origin, Android.BankBot.1002.origin) and Wroba (Android.Banker.360.origin) households. The Wroba household (Android.BankBot.907.origin) was additionally used to assault customers in Japan. And Android system homeowners from China have been attacked by the Android.Banker.480.origin trojan.
Our specialists, nevertheless, additionally noticed new traits in banking trojan assaults, one of the notable ones being the emergence of latest banking malware households, lots of which focused customers in Russia. Amongst them have been Android.Banker.5127 and Android.Banker.5273, which have been created with the assistance of the Tasker scheduling app; Android.Banker.597.origin, Android.Banker.592.origin, and Android.Banker.5235, which masqueraded as varied companies, together with — KoronaPay, Дайвинчик 18+ (Daivinchik 18+), Yandex, Rostelecom, and OnlyFans; and quite a few different trojans.
Assaults on Russian customers additionally concerned the usage of Android.Banker.637.origin, Android.Banker.632.origin, Android.Banker.633.origin, and Android.Banker.635.origin—banking trojans that menace actors distributed underneath the guise of quite a lot of apps. For instance, criminals handed them off as software program that was supposedly associated to totally different on-line streaming companies (like STAR), adult-only apps, mods of the VK social community official Android consumer, and thematic packages based mostly on the collection “The Boy’s Phrase. Blood on the asphalt” (“Слово Пацана. Кровь на асфальте”), which in 2023 gained recognition in Russia and international locations of the previous USSR, and so on.
Additionally widespread in Russia have been the banking trojans Android.BankBot.1062.origin, Android.BankBot.1093.origin, and Android.BankBot.1098.origin. These later expanded the geography of their assaults to incorporate customers in Uzbekistan.
On the similar time, Physician Net’s malware analysts famous the emergence of many banking trojans concentrating on Iranian customers. Amongst them have been Android.BankBot.1088.origin, Android.BankBot.14871, Android.BankBot.1083.origin, Android.Banker.5292, Android.Banker.5233, Android.Banker.5276, and Android.Banker.5379. Furthermore, malicious actors distributed Tambir Android banking trojans (Android.BankBot.1099.origin), which have been designed to assault Turkish Android system homeowners.
Noticeable exercise was additionally noticed from banking trojans of the Rewardsteal banking trojan household (Android.Banker.562.origin, Android.Banker.5138, Android.Banker.5141, Android.Banker.588.origin, Android.Banker.611.origin). Amongst these, the commonest modifications focused prospects of such banks as ICICI Financial institution, HDFC Financial institution, SBI, Axis financial institution, Citi financial institution, and RBL financial institution.
Prospects and traits
Since materials achieve stays the primary motivation for cybercriminals, we should always anticipate new malicious packages to emerge that may assist them improve their unlawful revenue in 2024. The almost definitely candidates for this is able to be extra adware trojans, banking malware, and rip-off and spy apps.
The chance of latest malware showing on Google Play will stay. And it’s doable that attackers will extra actively use different sources, malicious web sites particularly, to distribute Android threats.
We must also extremely anticipate the emergence of latest trojans designed to steal crypto forex from each Android system and iOS system homeowners.
To guard your self from prison assaults and to maintain your cash and private information protected, we advocate putting in Dr.Net anti-virus on all of your supported gadgets. For our half, we at Physician Net will proceed to observe traits within the cyber-threat panorama and inform our customers about necessary occasions within the discipline of knowledge safety.

Your Android wants safety.
Use Dr.Net
- The primary Russian anti-virus for Android
- Over 140 million downloads—simply from Google Play
- Out there freed from cost for customers of Dr.Net residence merchandise